Related Flashcards
Cards In This Set
| Front | Back |
|
Conflict
|
When one party feels that another party has or is about to negatively affect something the first party cares about.
|
|
Views on Conflict
|
Traditional ViewHuman Relations/Interactionist ViewManaged-conflict view
|
|
Traditional View
|
Conflict is bad and should be avoided at all times
|
|
Human Relations/interactionist View
|
Conflict is absolutely necessary for a group to perform effectively.
There is functional (good) and dysfunctional conflict (bad) |
|
Managed-conflict View
|
Instead of encouraging or discouraging conflict, you should resolve naturally occurring conflicts productively
|
|
Functional Conflict
|
Conflict that supports the foals of the group and improves its performance (creativity & innovation)
|
|
Dysfunctional Conflict
|
Conflict that hinders group performance
|
|
Potential Benefits of Conflict
|
Can lessen social tensionsCan prevent stagnation or groupthinkCan lead to resource re-allocation Can provide greater understanding of selfCan serve as a red flag
|
|
Perceived Conflict
|
Conflict that doesn't cause a tense or anxious experience
|
|
Felt Conflict
|
Conflict that is emotionally involved and causes tension, anxiety, and frustration
|
|
Conflict Resolution Techniques
|
Problem solvingSuperordinate goalsExpansion of resourcesavoidancesmoothingcompromise authoritative command
|
|
Conflict Stimulation Techniques
|
CommunicationBringing in outsidersRestructuring the organizationAppointing a devil's advocate
|
|
2 Conflict Handling Dimensions
|
Cooperativeness- degree to which one party attempts to satisfy the other party's concerns.
Assertiveness- degree to which one party attempts to satisfy their own concerns. |
|
5 Conflict Handling Intentions
|
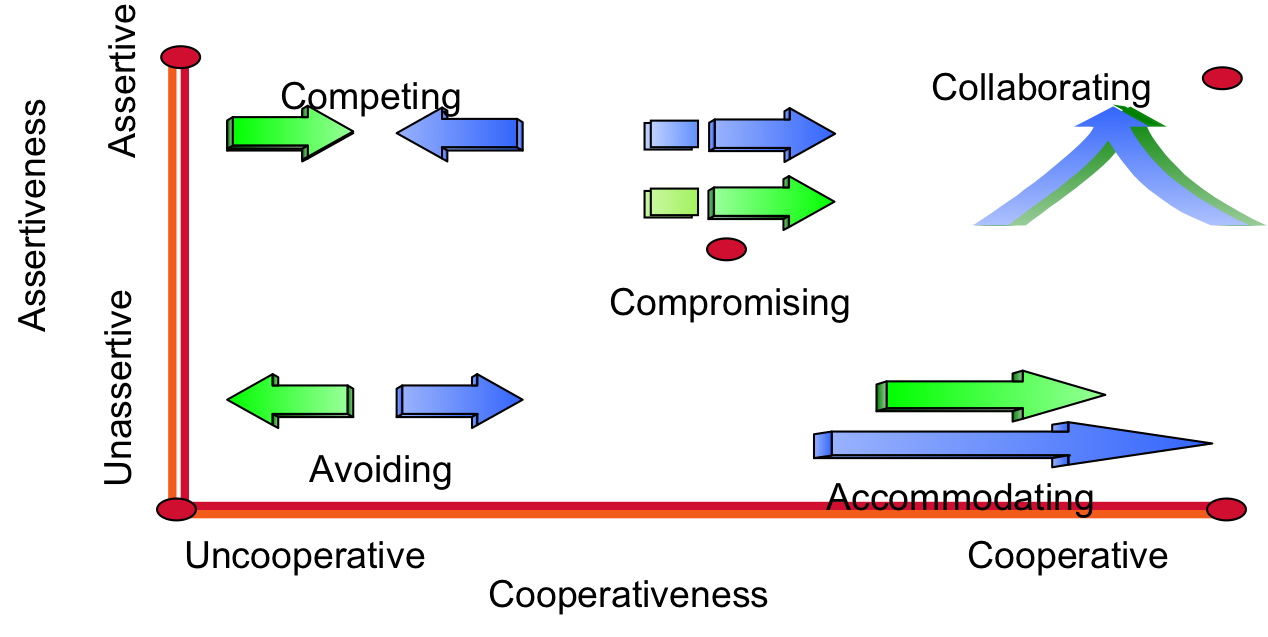 CompetingCompromisingCollaboratingAvoidingAccommodating |
|
Competing
|
Insisting your way. Use when you know you are 100% right.
|






