Related Flashcards
Related Topics
Cards In This Set
| Front | Back |
|
Duty of Loyalty
|
requires that directors act on behalf of the corporation and its shareholders and refrain from selfdealing,
|
|
Duty of Care
|
requires that directors discharge their duties in good faith and with the care that an ordinarily prudent person in a like position would exercise under similar circumstances and in a manner the director reasonably believes to be in the best interests of the corporation.
|
|
Technical Core
|
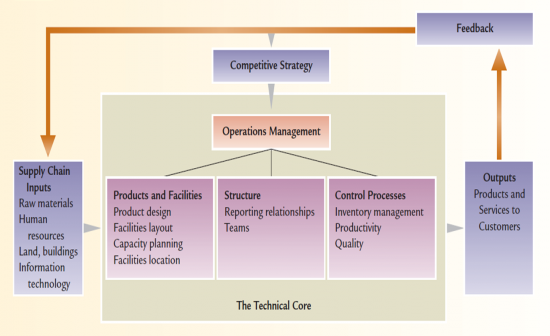 |
|
Service Organization
|
-Produces nonphysical outputs
-Quality percieved and difficult to measure -Customized output -Consumer participates in production process EG: Airlines, Hotels, Hospital |
|
Manufacturing Organization
|
-Produce physical goods
-Goods inventoried for later consumption -Standaridzed output -Production process removed from consumer EG:Automobile manufacturers, Steel Companies, Soft-drink companies |
|
Supply Chain Management
|
Managing the sequence of suppliersand purchasers, covering all stages of processing from obtaining raw materials to distributing finished goods
-A network of multiple businesses and individuals that are connected through the flow of product and services. -The main point is all of the activities that facilitate the satisfactory fullfillment of an order at the highest degree of satisfaction and the lowest possible cost. - Arms length approach: when an organization spreads purchases among many suppliers to encouragae them to compete. -Partnership approach: Picking one partner to work hand and hand to work cooridinate tasks and benefit both parties. From Book: |
|
Lean Thinking Inventory
|
Combining advanced technology and management process and using highly trained employees to solve problems, cut waste, improve productivity, quality, and efficiency of products and services, and increase customer value.
|
|
4 Functions of Management
|
1.) Planning:Identifying goals for future organizational performance and deciding on the tasks and use of resources needed to attain them.
2.) Organizing: assigning tasks, grouping tasks in departments, delegating authoroity, allocating resources across the organizations. 3.) Leading: the use of influence to motivate employees to achieve organizational goals. 4.) Controlling: Monitoring employees activities, determining whether the organization is on target toward its goals, and making corrections as necessary. |
|
The process of Management
|
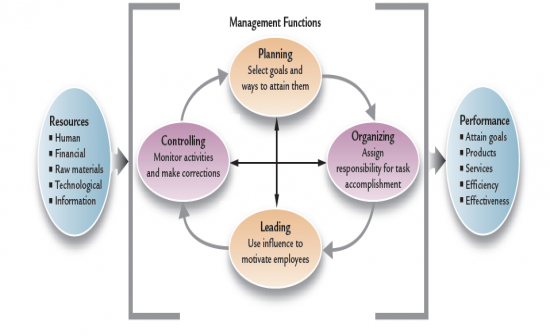 |
|
Organizational Performance
|
- Orginization: is a social entity that is goal directed and delibertly structures.
- Effectiveness: The degee to which the organization acheives a stated goal. -Efficiency: The amount of resources used to achieve an organizational goal. -Ultimate goal of a manager is to achieve high performance. |
|
Management Skills ( 3 categories)
|
- Conceptual Skills: The cognitive ability to see the organization as a whole system and the relationships among its parts. - Human Skills: Is the managers ability to work with and through other people and to worl effectily as a group member. - Technical Skills: Is the understanding of and proficiency of specific tasks. *** The application of mgmt skills change as managers move up in hierarchy. |
|
Top causes of Management Fails
|
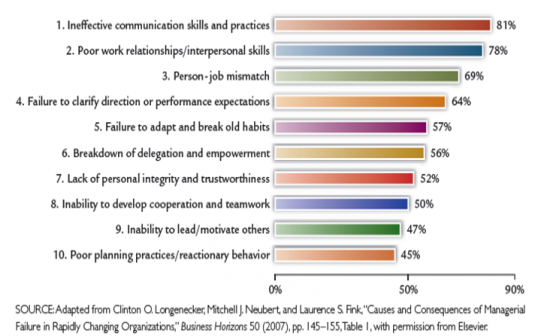 |
|
Management Types: Vertical
|
•Top managers are responsible for the entire organization
•Middle managers are responsible for business units •First-line managers are responsible for production of goods and services |
|
Management Types:Horizontal
|
•Functional Managers are responsible for departments that perform specific tasks
•General Managers are responsible for several departments |
|
Management Levels
|
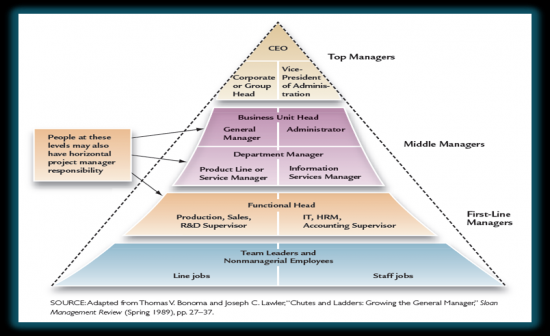 |





