Related Flashcards
Related Topics
Cards In This Set
| Front | Back |
|
Shock definition
|
Imbalance of cellular O2 delivery and cellular O2 demand which results in impaired tissue perfusion which may cause SBP <90 with tachycardia or bradycardia and altered mental status.
|
|
Stages of Shock
|
Inital, Compensatory, Progressive, Refactory
|
|
Pathophysiology of Shock (Inital Stage)
|
Decreased CO/Tissue perfusion which leads to anerobic metabolism which leads to small amount of energy/lactic acid peroduction, which leads to increased cellular damage.
|
|
Pathophysiology of Shock (Compensatory Stage)
|
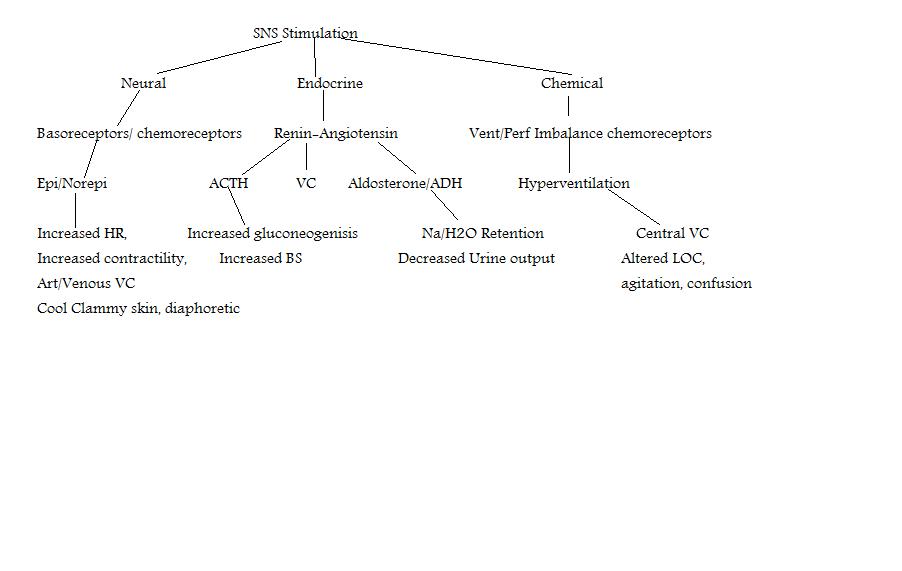 See concept map |
|
Pathophysiology of Shock (Progressive Stage)
|
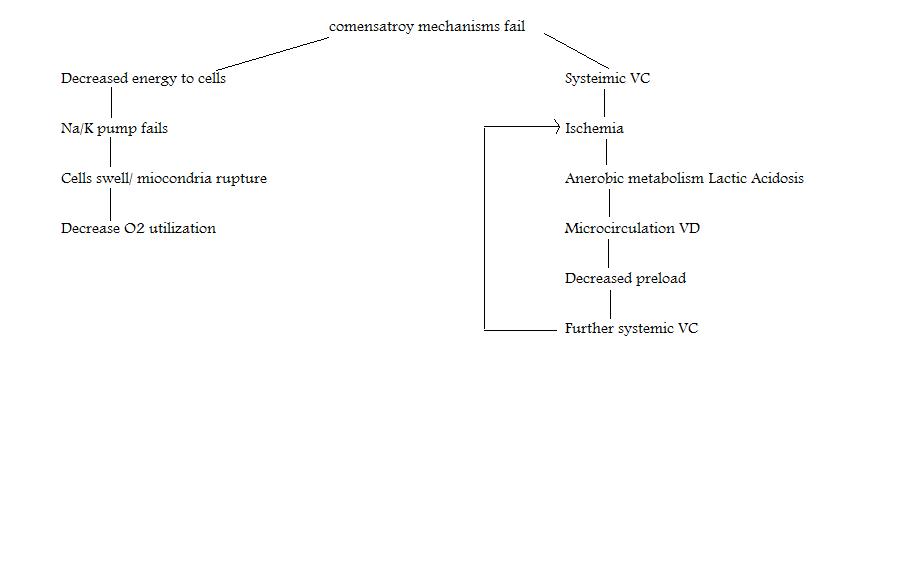 See concept map |
|
Pathophysiology of Shock (Refactory Stage)
|
Prolonged decreased tissue perfusion, peripheral blood pooling, decreased vital organ perfusion, acidosis.
Unresponsive to therapy, irriversable.
MODS: failure of two or more body systems
CV- Ventricular Failure
CNS- SNS failure=vasodialtion=capillary pooling, increased capillary permeability, microemboli
Hematologic- DIC
Pulmonary- ARDS, Resp failure
Renal -ATN
GI- failure gut organs= release gram negative bacteria into system
|
|
Hyopvolemic Shock
|
Inadequate circulating fluid volume in intravascualr space, most common form of shock,
absolute- external loss of fluid
relative- internal shifting of fluid within body
|
|
Hypovolemic Shock Inital Stage
|
CO maintained, symptom free, approximately 750ml
|
|
Hypovolemic Shock Compensatory Stage
|
750-1500 ml loss. CO decreases, tachycardia, narrow pulse pressure (VC), RR/depth increase, ABG: resp alkalosis, hypoxemia, UO decreases, skin pale, cool, capilary refill > 3 sec altered LOC
|
|
Hypovolemic Shock Progressive Shock
|
1500-2000 ml loss, tachycardia, dysrhythmias, ABG: resp & metabolic acidosis, hypoxemia, resp. distress, oliguria, BUN & Creatinine increase, skin; ashen, cold, clammy marked delayed cap refill and lethargy
|
|
Hypovolemic Shock Refractory Stage
|
>2000 ml loss, severe tachycardia, hypotension, peripheral pulses absent, no cap refill, skin: cyanotic, mottled, diaphoretic, unresponsive.
|
|
Hypovolemic Shock Hemodynamic Parameters
|
Decresed CO/CI
Decreased CVP/RAP
Decreased PAP, PAOP
Decreased SVO2
Increased SVR
|
|
Hypovolemic Shock Therapy
|
Medical- Stop source of fluid loss and replace ciruclating volume with crystalloid (NS, D5W, D51/2), colloid (albumin, dextran, hestran), or autotransfusion
nursing- prevention, I/O, daily wts, minimize fluid loss (limit blood sampling, secure connection of lines, direct pressure to bleeding sites), enhance fluid replacement (large bore IV, rapid administration of fluids, trendelenburg, monitor for fluid overload)
|
|
Cardiogenic Shock
|
Failure of heart to pump effectivly 6-20% of AMI 72-84% mortality, ventricular ischemia, sturctural, dysrhythmias.
|
|
Cardiogenic Shock pathophysiology
|
Decreased pump,
decreased SV=decreased CO= decreased Cellular O2 Supply= ineffective tissue perfusion,
LHF=pulmonary edema=impaired gas exchange=decreased O2 of arterial blood= impaired tissue perfusion
|