Cards In This Set
| Front | Back |
|
Virus
|
- A oobligate parasite because it has to enter a host before it can replicate
|
|
Herpes Virus- Types
|
- Herpes Simplex Virus 1
-Herpes Simplex Virus 2 -Varicella-Zoster Virus -Epstein-Bar Virus -Cytomegalovirus |
|
Herpes Simplex Virus
|
-Lytic to epithelial cells
-Latent in neural tissue -Enters the body through breaks in the skin, but can penetrate intact mucous membranes -HSV1 above the waist -HSV2 below the waist |
|
Acute Primary Herpetic Gingivostomatitis
|
 -1% of initial oral infections with HSV1 & 2 have symptomatic primary infection - Usually occur in young children - Multiple small, punctate, shallow ulcers involving the gingiva, lips, perioralskin and/or nasopharynx - Severe forms have large, diffuse, white ulcers that have scalloped borders and erythematoushalos - May experience muscle soreness(myalgia) and inability to masticate and swallow food - Immunocompromisedpatients may have prolonged form with larger and deeper lesions |
|
Acute Primary Herpetic Gingivostomatitis
|
 |
|
Secondary Oral herpes Simplex
-Recurrent oral herpes simplex types |
-Labialis
-Intraoral -Both are associated with recent dental treatment |
|
Recurrent Herpes Labialis
|
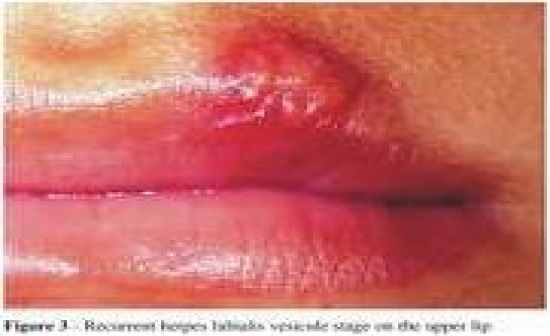 -Most common form of recurrent HSV infections - “Cold sore” because it often occurs after an UR infection - Reactivation sunlight, trauma and manipulations of the lips, fever, immunosuppression, menstruation and stress/anxiety - Cover with ointment to prevent further spreading and secondary bacterial infection |
|
Recurrent Intraoral Herpes
|
 - Uncommon and often occurs post dental treatment or injections - Most common site is the hard palate over the greater palatine foramen |
|
Neonatal Herpes Simplex Virus
|
 - Most frequent in infant born during primary HSV infection - Commonly involve the skin, eyes and mouth - Caesarean sections recommended with clincialevidence of active herpes lesions on the cervix or vulva |
|
Herpetic Whitlow
|
 - Herpes simplex infection on the hand acquired by direct contact with an active lesion - Throbbing pain, high fever, and regional lymphandenopathyof the arm - Systems may incapacitate the patient for 1 or more weeks - Very contagious |
|
Varicella-Zoster Virus
|
-Primary infection- varicella(chicken pox)
-Secondary infection- shingles
-Herpes virus
-Fluid filled vesicles on the skin or mucosa
-Mode of contact- inhalation of droplets
|
|
Varicella
|
 - Primary infection of VZV usually acquired in childhood -2 week incubation - Hemorrhagic maculopapularrash with malaise and low grade fever - Lesion progress to pustules and vesicles that rupture and become crusted - If acquired during adulthood cases can be severe and progress into interstitial pneumonia |
|
Herpes Zoster (Shingles)
|
 -Recurrent form of Varicella-Zoster virus - 10-20% of population, more common in elderly and immunocompromised - Trigeminal nerve involvement unilateral face and oral lesions may develop along the opthalmic, maxillary and mandibulardivision of the nerve - Intraoral lesions are sharply unilateral and are fragile vesicle that rupture easily lasting 2-3 weeks - Pains, paresthesia, dyesthesia - Pain may persist for 1+ months after lesions have healed (burning & severe pain) and remain hypersensitive for years and can be highly debilitating - Ramsey-Hunt syndrome- involves 3 conditions of ipsilateralfacial palsy, external auditory canal lesions and loss of taste in the anterior 2/3 of the tongue - Antiviral meds are most effective when started within 72 hours after the onset of the rash |
|
Epstein Barr Virus
|
- Herpes virus know to cause infectious mononucleosis, Burkittlymphoma and nasopharyngeal carcinoma
- Virus found in HPV in the nose, in AIDS patients in the hairy leukoplakiaof the tongue and lymphomas
- Transmitted through saliva
- 90% of population carry
|
|
Burkitt Lymphoma
|
 |



