Cards In This Set
| Front | Back |
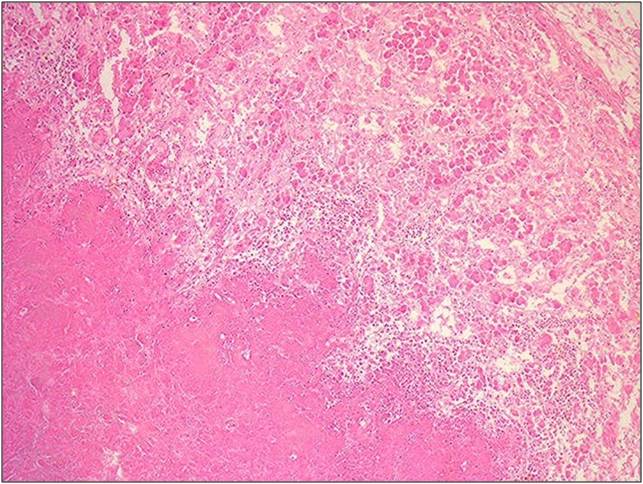 Identify |
Caseous necrosis
Tuberculosis 16 and 371 “Cheeselike” Irregular fever treated with erythromyocin Extreme pink area Lymph node biopsy |
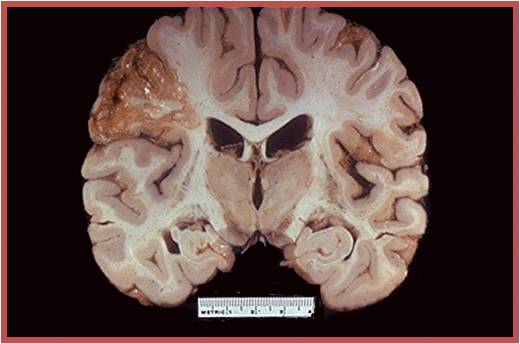 Identify |
Brain necrosis
•Cell death •Liquefactive necrosis (15) •Also seen in kidney |
 Identify |
•Enzymatic Fat necrosis (16)--pancreas
•Chalky white areas*****
•Alcohol
•Activation of trypsinogen and then sequential changes
•Causes of acute pancreatitis (893)
•Know alcohol is a
reason
•Purple box (894)
•Alcoholism is associated with acute pancreatitis, what
else can be a cause? (see table-893)
Coxsackie virus |
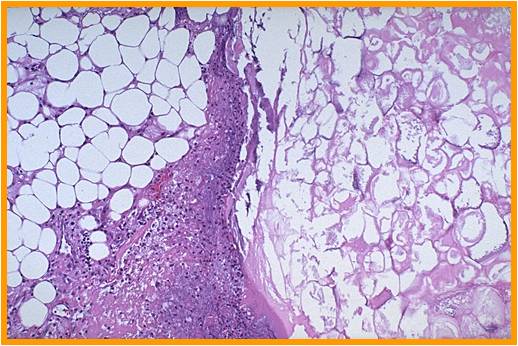 Identify |
•Enzymatic Fat necrosis
•Visual (894)
•3 compartments
•Area 1 (far
left)-preserved fat
•Area 2
(middle)-inflammatory cells
•Area 3 (right)-hazy
fat,
•1 and 3 contain fat (adipocytes) 1 is not digested/dead=viable, 3 is dead fat
(enzymatic fat necrosis)
•2 is composed of acute and chronic inflammatory cells
|
 Identify |
•Widening of the sulci
and narrowing of gyri******
•Visual-atheroslcerotic cerebrovascular disease (9)
•No question related to alzheimers
•From reduced blood supply
|
 Identify |
•Left=normal homogenous and uniform
•Right=atrophic
•Klinefelter
•Regressive changes
(985)
•Athlerosclerotic
•Hypopituitaism
•Inflammatory orchitis (mumps)
•Crytorchidism
•Malnutrition and cachexia
•Irradiation
•Antiandrogens
•Exhaustion atrophy
(too much FSH)
|
 Identify |
Lipofuschin pigment as residual bodies
•Atrophy-liver biopsy •Hepatocytes contain brown pigment=lipofuscin •Residual bodies •Gives brown color •Hepatocytes that do not contain brown pigment=they ALL have brown pigment •Mechanisms of Atrophy (10) •Brown atrophy |
 Identify |
•Ventricular wall
•Normal dimensions (530)
•RV=0.3-0.5 cm
•LV=1.3-1.5 cm
•Hypertrophy of the heart (7)
•ANF expressed in both
the atrium and ventricle in embryonic heart
•Reinduction of ANF later in life
causes hypertrophy
•Systemic
hypertension=work related hypertrophy
|
 Identify |
•Compresses prosthetic urethra
•Prostate needs to be removed=prostectomy—cystoscope= turp transurethral
resection of prostate
•BPH (995); prostatic hyperplasia is always pathological
•Visual (993)
•Nodular hyperplasia
•Split=prostatic urethra
•Excess Androgens
cause this
•Male pt after >60 having trouble urinating
•Central slit was prostatic urethra
•Prostatic secretions are known as corpora amylacae
•An elevated PSA is organ specific but not cancer
specific
|
 Identify |
Prostatic hyperplasia (microscopic appearance)
Enlarged prostate •Gladular epithelium and stroma on the left •Prostate gland produces Corpora Amylacea •Circles=lumens and the pink in them is the secretions Normal prostate and enlarged prostate have 2 cells •Double layer lining epithelium (lost in enlarged=only have one layer) •Regular round nucleus near BM •Normal has double lining •Prostatic Carcinoma=one lining**** •Prostate normally has double layered epithelium w/ 2 nuclei •Prostatic cancer usually goes to the bonesàback pain |
 Identify |
Endometrial Hyperplasia
•Historectomy specimen=uterus surgically removes (45 year old) •Cervix at the bottom •Endometrial cavity •Endometrial Hyperplasia (1030) •Mutation of PTEN in hyperplasia and carcinoma of endometrium •Hormone therapy for young women with hyperplasia (21 year old) (for fixed estrogen levels) •21 year old student with profuse bleeding. •45 year old woman w/ 5 children with profuse bleeding |
 Identify |
Barrett Esophagus
•Sqaumous cells on the right (squamous=normal) pg 10 •45 year old chronic smoker, likes spicy food, develops pain in epigastric. Some days he responds, somedays he doesn’t •Glandular Columnar goblet epithelium cells on left (adenocarcinoma region) •Barrett Esophagus (770) •Intestinal metaplasia •Lower part of the esophagus •Confers an increased risk of esophageal adenocarcinoma •Zone 1 (left) •Intestinal epithelium with goblet cells •Vacuolated cells goes in favor of goblet cells •Zone 2 (right) •Squamous cells |
 Identify |
Myocardial Infarction
•Cardiac muscle •Infarction=type of necrosis •Pink irregular bundles=dead myocardial fibers •Cells in between=inflammatory cells •Table (550) •Inflammatory cells (neutrophils) appear 12-24 hours •Fibers have lost their nucleus=special feature of ischemic necrosis (coagulative necrosis) •Ischemic cell death |
 Identify |
Contraction Bands
•Bands=contraction bands which appear when cellular proteins undergo coagulation •Image C (554) •Some inflammatory cells •Acellular myocardial cells indicate cell death •Table (550) •Contraction bands appear 12-24 hours •Died of MI |
 Identify |
Infarction kidney
White infarct •Occlusion=renal artery •Wedge shaped •Artery infarcts are white •Venous infarcts are red |



