Cards In This Set
| Front | Back |
 Identify |
Acute inflammation. See neutrophils (trilobed)
|
 Identify |
Early (neutrophilic) (left) and later
(mononuclear) cellular infiltrates (right) of infarcted myocardium
|
 Identify |
Margination & diapedesis of neutrophils
|
 Identify |
Exudation
Vasodilation with exudation has led to an outpouring of fluid with fibrin into alveolar spaces, along with PMN's. |
 Idenfity |
Exudation of fibrin
Fibrin mesh in fluid with PMN's in acute inflammation that produces "tumor" or swelling of acute inflammation |
 Identify |
Serous inflammation
•Thin, watery exudate with insufficient amounts of fibrinogen to form fibrin material. eg. blister fluid |
 Identify |
•Fibrinogen-rich
exudate that forms excess fibrin
•“Bread
and butter” appearance on serosal surfaces
•eg. fibrinous pericarditis
|
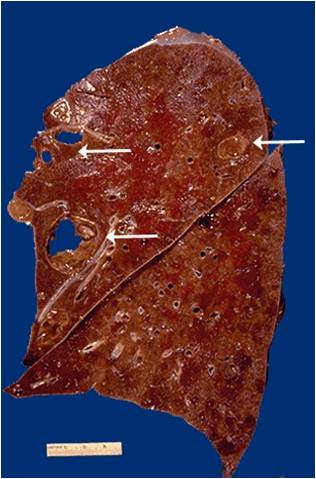 ID |
•Localized
collection of pus (liquefactive necrosis) with formation of an abscess
•eg. Lung abscess
–Liquefactive necrosis seen - purulent contents drain
out leaving a cavity. Chest X-ray – Liquefied central contents
appear as an "air-fluid level".
|
 Id |
Toxin induced superficial mucosal damage. Formation of a nectrotic membrane along a mucosal surface. Pseudomembranous inflammation. Pseudomembrane colitis, pseudomembrane of diptheria
|
 ID |
Acute bronchopneumonia.
PMNs form an exudate in the alveoli |
 Identify |
Acute cholecystitis.
Neutrophils infiltrating mucosa and submuscosa of the gallbladder. |
|
ID
|
Granulomatous inflammation. Seen in TB and sarcoidosis.
|
|
ID
|
Foreign body granuloma
|
|
ID
|
Alveoli, cells with neutrophils. Broncopneumonia- exudative inflammation
|
|
ID
|
Granulomatous inflammation
|



