Cards In This Set
| Front | Back |
 Identify  |
Physiologic hypertrophy of the uterus
|
 Identify |
Normal uterus
|
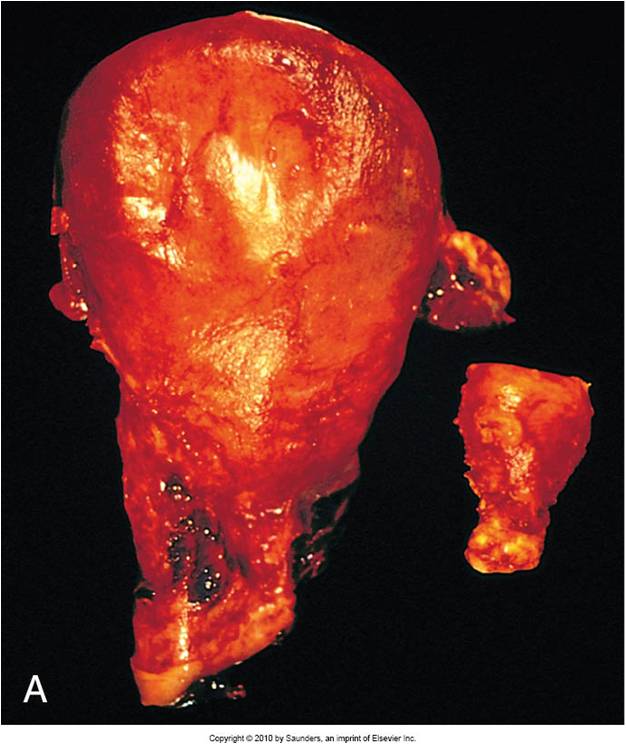
 Identify |
Gravid uterus
|
 Identify |
Normal brain of young adult
|
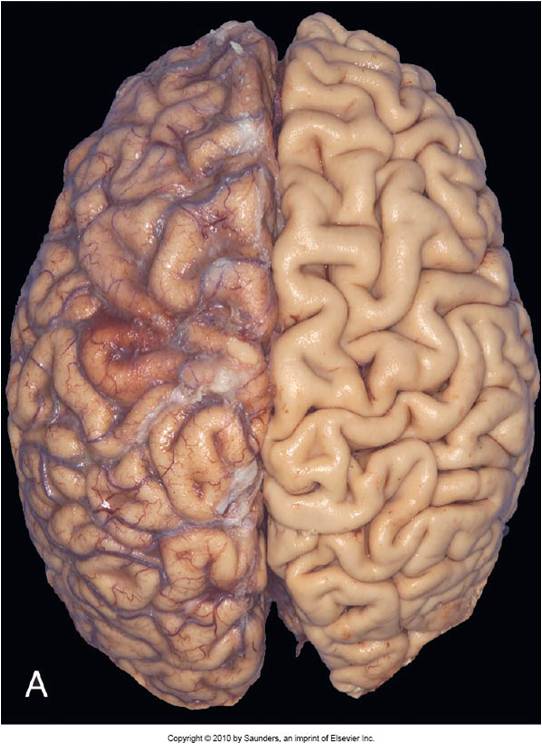
 Identify |
Atrophy of brain of 82 year old with atherosclerotic cerebrovascular disease resulting in reduced blood supply
Narrow gyri, widening of sulci |
 Identify |
Metaplasia of columnar epithelium to squamous epithelium in bronchus qw321
|
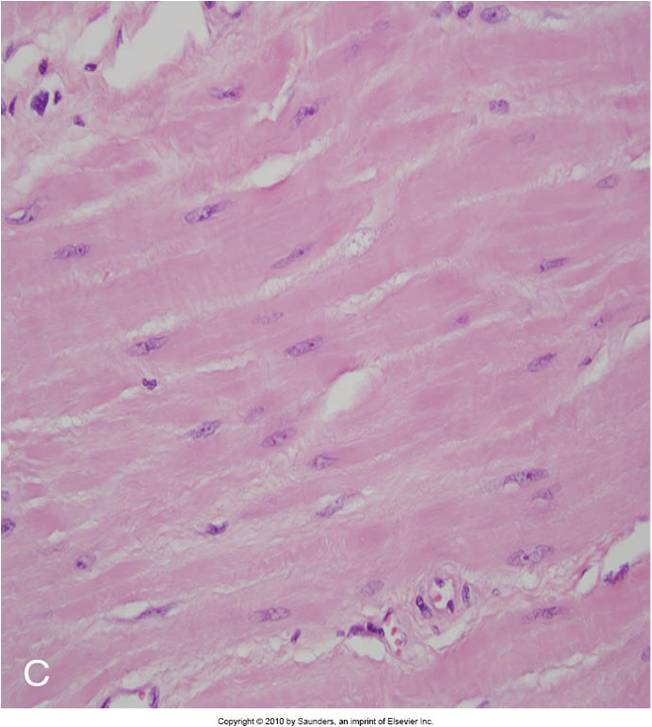
 Identify |
Normal kidney tubule with viable epithelial cells
|
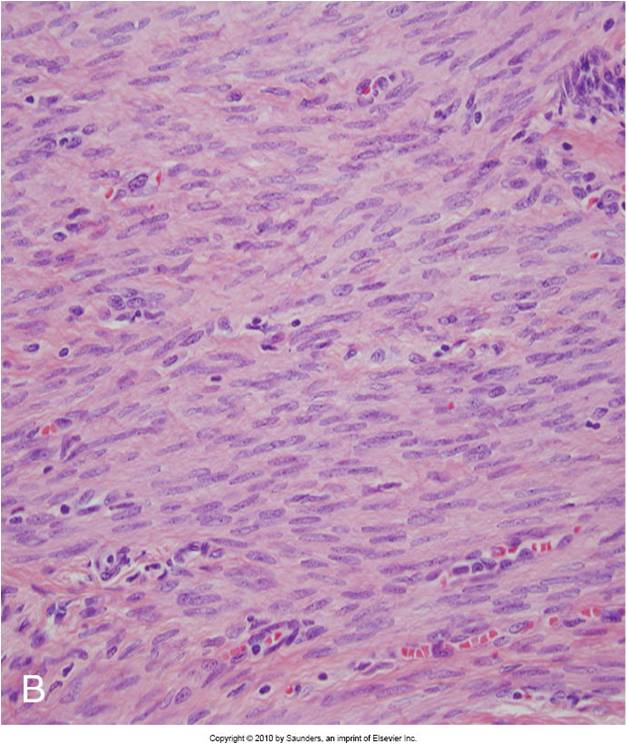
 Identify |
Early reversible ischemic injury showing surface blebs, increased eosinophilia of cytoplasm, swelling of occasional cells
|
 Identify |
Electron microscope of a normal epithelial cell of the proximal kidney tubule. Abundant microvilli lining the luminal surface.
|
 Identify |
Epithelial cell of the proximal tubule showing early cell injury. Microvilli are lost and incorporated in apical cytoplasm. blems have been formed and extruded in the lumen.
|
 Identify |
Necrosis of epithelial cells, loss of nuclei, fragmentation of cell, leakage of contents
|
|
Identify
|
Necrotic cell w/ black spots representing electron dense deposits in mitochondria.
|
|
Identify
|
Wedge shaped area is area of infarct in cross section of kidney.
|
|
Identify
|
Microscopic view of the edge of infarct with normal kidney (n) and necrotic cells in (i) showing preserved cellular outlines with loss of nuclei and an inflammatory infiltrate.
|
|
Identify
|
Fibrinoid necrosis in an artery.
|



