Cards In This Set
| Front | Back |
|
Essential Nutrients
|
Substances that the body must get from food because it cannot manufacture it or cannot make enough of it to fit its needs
-there are 45 essential nutrients- 6 catagories
|
|
6 catagories of Essential Nutriends
|
-Proteins
-Fats
-Carbohydrates
-Vitamins
-Minerals
-Water
|
|
Protein
|
- Proteins form key parts of the body's main structural components- bones and muscles- and of blood, enzymes, cell membranes, and some hormones
--Protein is made up of amino acids
- 1g protein = 4kcal
|
|
Types of Protein, intake
|
- Complete- from meat sources
- Incomplete- from plant sources, beans, penut butter,
-.8g/kg of body weight per day
|
|
Fats
|
-also known as lipids, supply energy, insulate the body, support and cusion organs, absorb fat soluble vitamins, and flavor and textures to food
-Types of Fat
-- unsaturated
-----monounsaturated
-----polyunsaturated
--saturated
-Intake
---Men- 17g of linoleic acid and 1.6g of alpha linolic acid
---WOmen 12g of linoleic acid and 1.1g of alpha linolic acid
|
|
Trans Fat
|
- unsaturated fatty acid produced during the process of hydrogenation
-hydrogenation is a process in which hydrogen is added to unsaturated fats, turning liquid fats to solids
-many prepared foods use this process
-in large amounts trans fats can lower HDL (good cholesterol) and promote risk of heart disease
- for heart health it is important to limit your intake of trans and saturated fats
- 1g fat -9 kcals
|
|
Types of fatty acids and effects on health
|
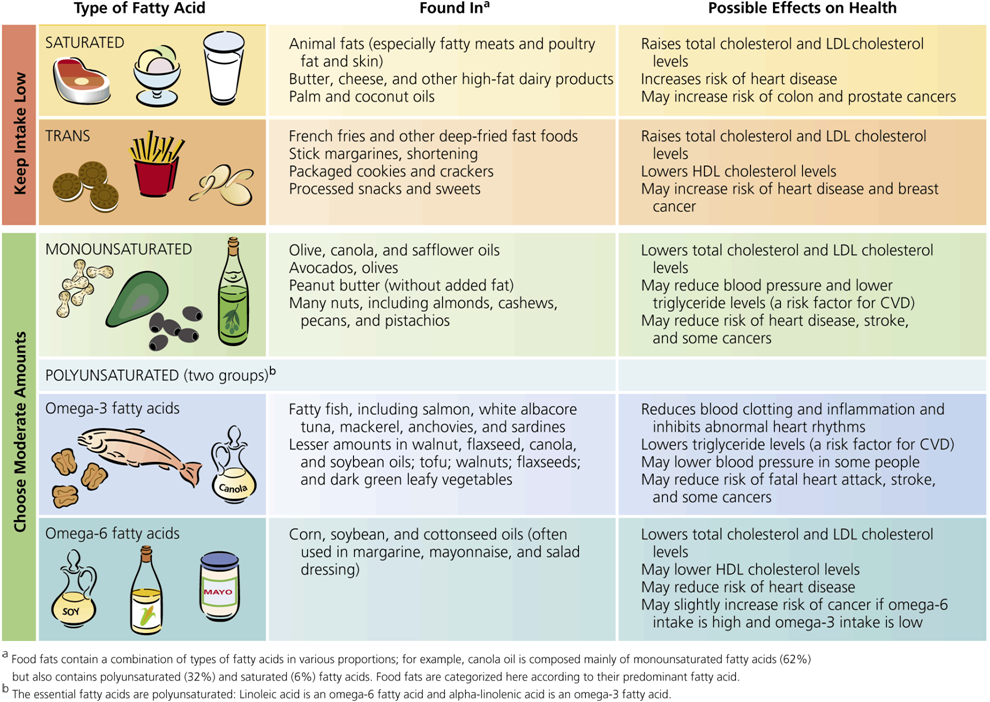 - |
|
Fats and Health
|
- most americans consume more saturated fats than trans fats which lower HDL and raise LDL
-monounsaturated and polyunsaturated fats have a number of heart healthy effects and can improve cholesterol
-in addiction to heart disease, dietary fats from red meat can raise risk of cancer, especially colon cancer
|
|
Carbohydrates
|
- the primary purpose of carbohydrates are to supply energy to the body cells
- 4 kcal/ 1g
-Two main types
---Simple (one or two sugar units/molecule)
---Complex (more than two sugar units/molecule)
-recommended levels: 225-325g in a 2000 calorie diet
- carbohydrates are broken down to glucose it their simplest form
|
|
Whole Grains
|
- have higher nutritional values compared to refined carbohydrates in the following
----fiber, vitamins, minerals, and other beneficial compounds
- whole grains take longer to chew and digest resulting:
----making people feel fuller sooner
----enter bloodstream more slowly
----reduce possiblilty of overeating
----slower rise in blood sugar
|
|
Glycemic index
|
- measure of how the ingestion of a particular food affects blood glucose levels
-foods with a high glycemic index cause a dramatic and quick rise in blood sugar
-diets rich in foods with a high glycemic index increase risk of diabetes, heart disease and increasing calorie intake
- high fiber foods and unrefined carbs have lower glycemic indexes
|
|
Fiber
|
-dietary fiber- indegestible carbohydrates that are intact in plant sources
-fiber passes through the intestinal tract and provide bulk for feces assisting with bowl elimination
-Types of Fiber
---Soluble Fiber: slows the body's absorption of glucose, binding cholesterol-containing compounds in the intestines
---Insoluble Fiber: binds with water, allowing fecal matter to become bulkier and softer
-Sources of Dietary Fiber- all plant food contains fiber, however fruits, legumes, and oats contain higher fiber amounts
-RDA for Fiber
- 38g in men
-25g in women
|
|
Vitamins
|
- organic (carbon- containing) nutrients needed in small amounts to help promote and regulate chemical reactions and processes in the body
-Types of Vitamins:
---Fat Soluble (A, D, E, and K)
---water soluble (C, the 8 B-complex vitamins, and pantothenic acid)
-sources of vitamins- fruits, vegetables, grains... also in some processed foods
|
|
Minerals
|
- inorgainc (non cabon containing) compounds needed in small amounts for regulation, growth, and matenance of body tissues and functions
-
|
|
Types of Minerals
|
- 17 essential minerals
- Major minerals- those that the body needs 100mg or more of a day-- calcium, phosphorus, magnesium, sodium, potassium, and chloride)
- Essential trace minerals- necessary in small amounts- copper, flouride, iron, iodide, selenium, and zinc
|



