Related Flashcards
Related Topics
Cards In This Set
| Front | Back |
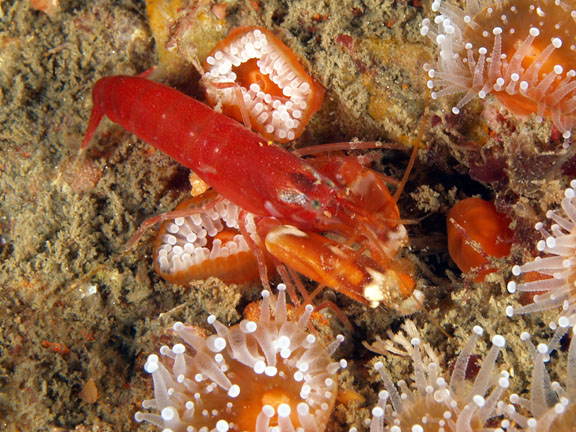 Phylum: Class: |
Phylum:
Arthropoda
Class:
Crustacea
|
 Phylum: Class: What is the difference between these cells and human red blood cells? |
Chordata
Amphibia human red blood cells lack nuclei |
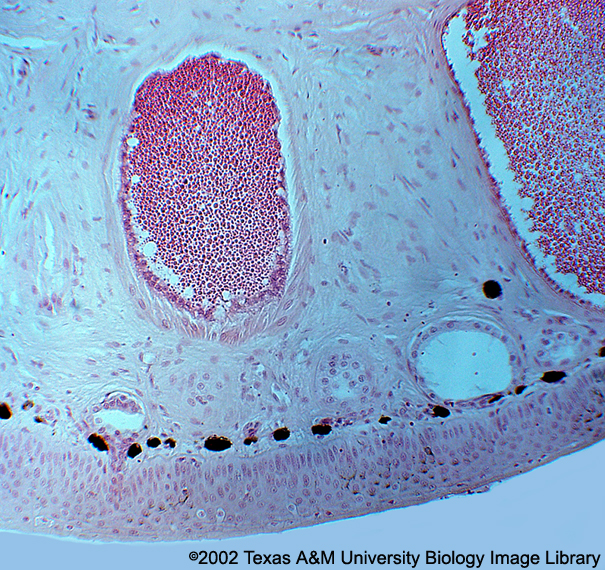 Class: Phylum: What skin type is this? How does it differ from shark skin?  |
Chordata
Amphibia Frog Lacks placoid scales |
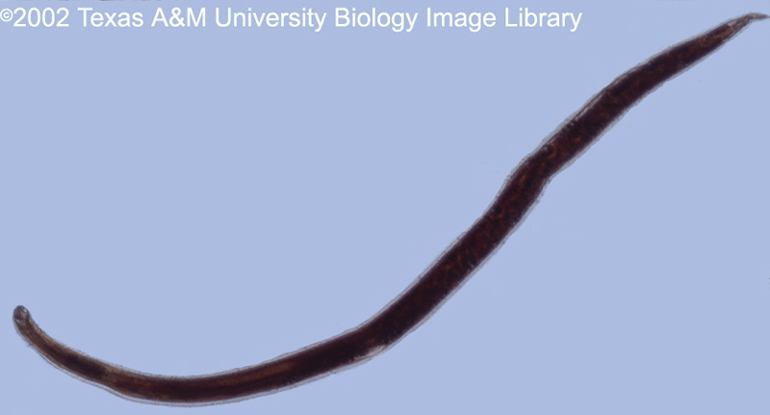 Phylum: Based upon your study of Nematodes, is this specimen a male or female? Explain. |
Nematoda
Female, posterior end is not curved or hooked |
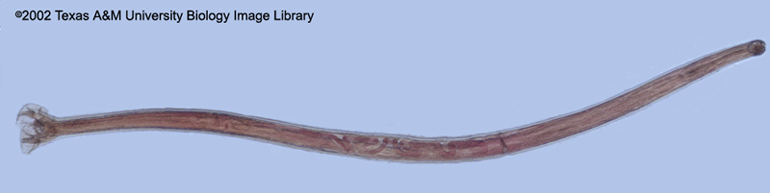 Phylum: Based upon your study of Nematodes, is this specimen a male or female? Explain. |
Nematoda
Male, posterior end is curved or hooked |
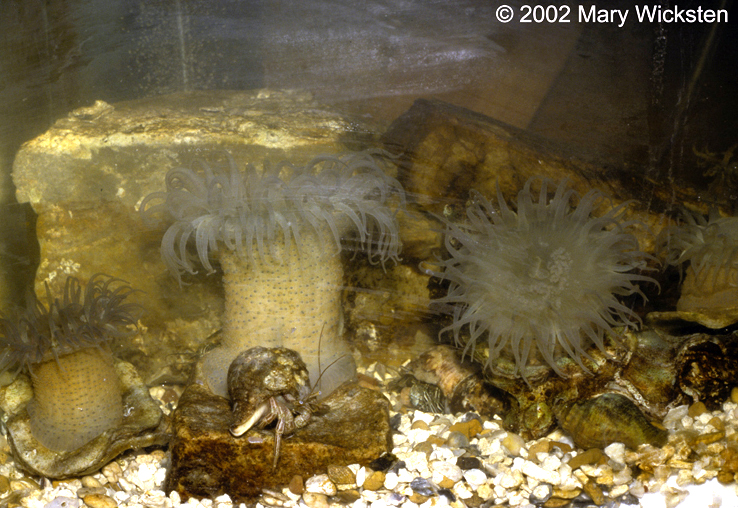 Phylum: (2) Class: (2) |
Cnidaria - anthozoa
Arthropoda - crustacea |
 Phylum: Class: Why is this coral considered to be a (phylum)? |
Cnidaria
Anthozoa It has polyps with nematocysts |
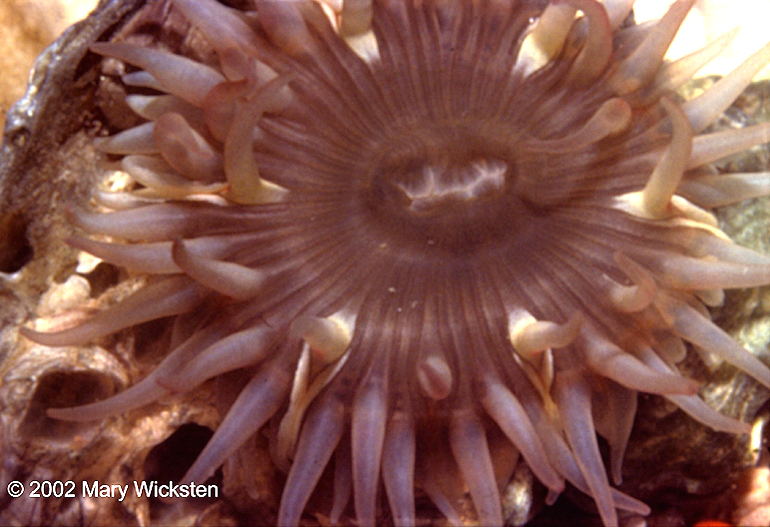 Phylum: Class: What is the name of the stinging cells on the tentacles of this organism |
Cnidaria
Anthozoa Nematocysts |
 Phylum: Class: Hard corals such as this stony coral have a skeleton made of what material (& are called) |
Cnidaria
Anthozoa Calcium Carbonate (Calcarea) |
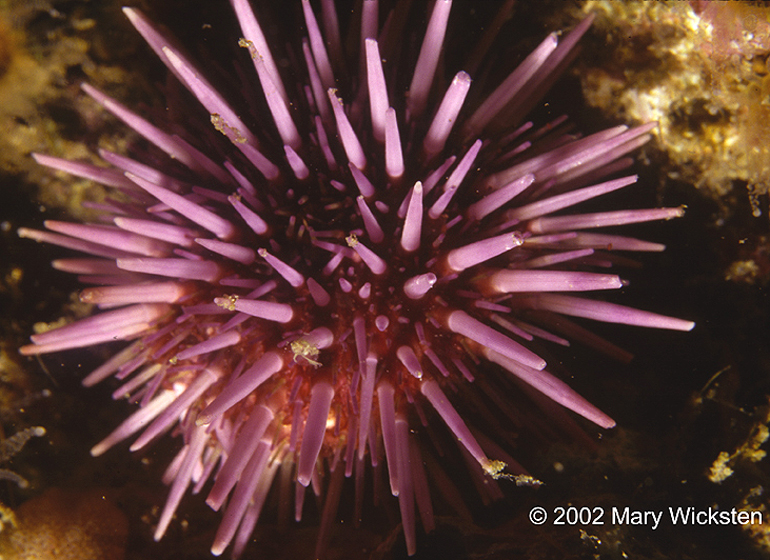 Phylum: Class: |
Echinodermata
Echinoidia |
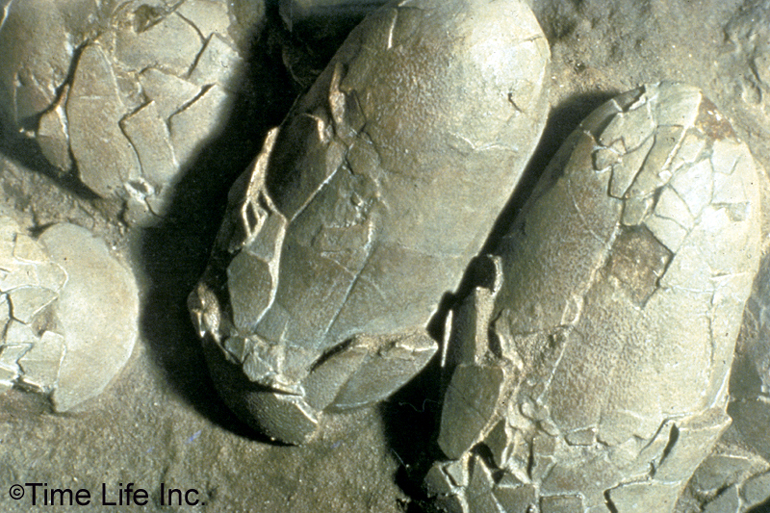 Were these fossil eggs most likely amniotic? |
Yes, observe the fossil layers. Also modern reptiles and birds lay
amniotic eggs which was an essential adaptation terrestrial habitats
|
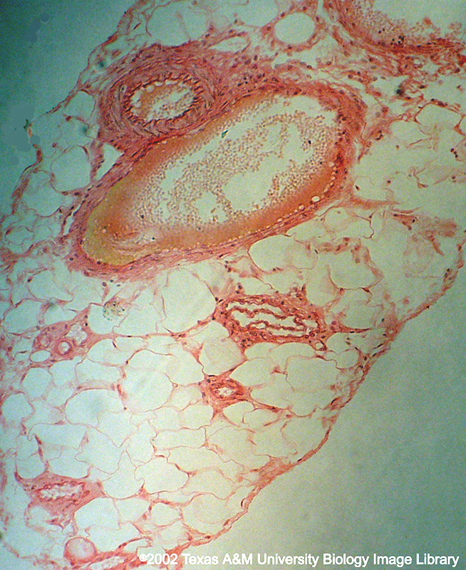 How do arteries, veins and capillaries differ morphologically and functionally? Identify one of each on this image. |
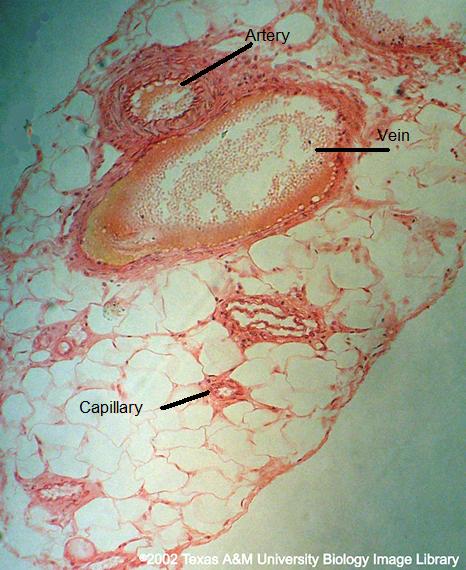 Artery: thick walls; move blood away from heart Vein: thin walls; bring blood to heart Capillary: thin walls; diffuse O2 & CO2 |
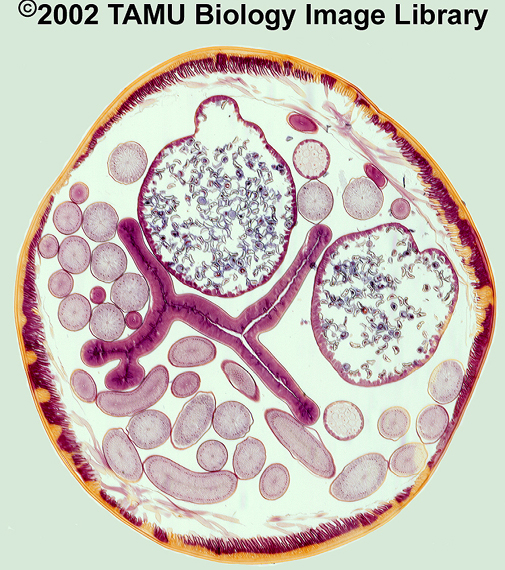 Identify: intestine, uterus, epidermis, ovary and pseudocoelom |
 See image |
 What type of body plan is represented by this organism? |
Pseudocoelomate
|
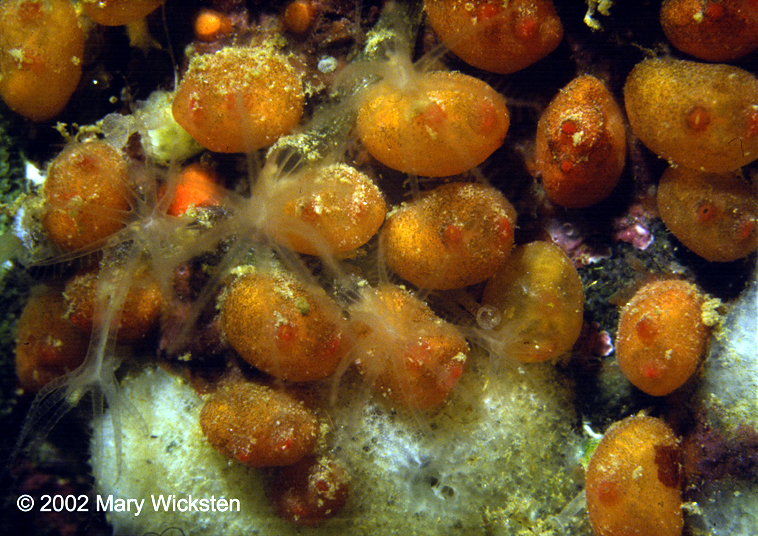 As adults these organisms lose most of their chordate characteristics. To what subphylum do they belong? |
Urochordata
|




