Related Flashcards
Related Topics
Cards In This Set
| Front | Back |
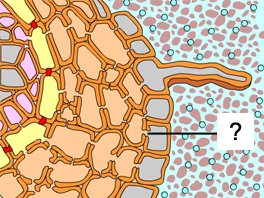 Channels, such as those indicated by the pointer, are _____. |
Plasmodesmata
|
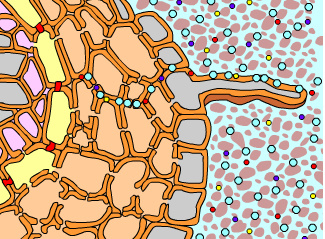 Which of these are symbiotic associations? |
Mycorrhizae
|
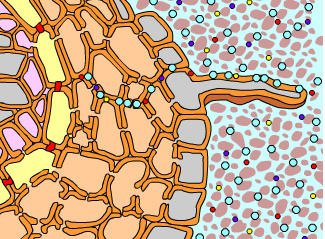 This is an animation of the movement of water and ions through the root _____. |
via the apoplastic route
|
|
N roots the _____ forces water and solutes to pass through the plasma membranes of _____ cells before entering the _____.
|
Casparian strip ... endodermis ... xylem
|
|
_____ provide(s) the major force for the movement of water and solutes from roots to leaves.
|
Transpiration
|
|
_____ bonds are responsible for the cohesion of water molecules.
|
Hydrogen
|
|
_____ cells are the cells that regulate the opening and closing of stomata, thus playing a role in regulating transpiration.
|
Guard
|
|
Which of these processes is responsible for leaves being considered sugar sources?
|
Photosynthesis
|
|
_____ transport(s) sugars from leaves to, for example, taproots.
|
Phloem
|
|
Sugar moves from leaves into the _____ of _____ by _____.
|
Sieve-tube elements ... phloem ... active transport
|
|
The water pressure that pushes water and sugar from sugar source to sugar sink is referred to as _____.
|
Bulk flow
|
|
Water moves into phloem by _____.
|
Osmosis
|
|
At a sugar sink, sugar is removed from phloem by _____.
|
Active transport
|
|
In a sugar sink, such as a taproot, sugar is converted into _____.
|
Starch
|
|
_____ is responsible for the movement of sugars from leaves to taproots; _____ is responsible for the movements of sugar from taproots to leaves.
|
Bulk flow ... bulk flow
|






