Cards In This Set
| Front | Back |
|
What composes the shoulder girdle?
|
Scapula and clavicle
|
|
Bones found in the Upper extremity?
|
Humerus, Radius and Ulna, carpals, Metacarpals, Phalanges
|
|
The head of the humerus attaches to ____
|
Glenoid cavity of scapula
|
 Identify: the greater and lesser tubercle headneckand intertubercular groove |
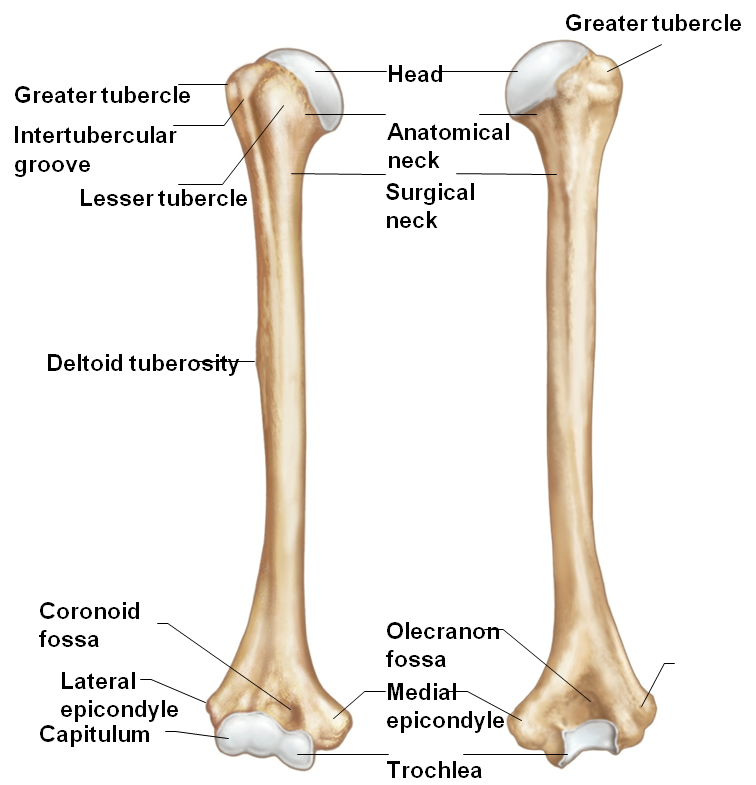 Picter |
|
What attaches to the deltoid tuberosity?
|
Deltoid muscle
|
|
What are the condyles called on the radius and ulna?
|
Capitulum (lateral)--RadiusTrochlea (medial)--Ulna
|
|
What are the two fossa located on the humerus?
|
Coronoid fossa -anteriorolecranon fossa- posterior
|
|
What three joints are located on the shoulder?
|
Sternoclavicular jointAcromioclavicular jointGlenohumeral joint
|
|
Where is the sternoclavicular joint and what is its importance?
|
Sternoclavicular joint is between clavicle and manubrium. it is important because it is the only attachment between UE and axial skeleton
|
|
Where is the acromioclavicular joint?
|
B/w the acromian of scapula and clavilcle
|
|
What kind of joint is the glenohumeral joint? and where is it located?
|
Ball and socket jointlocated between head of humerus and glenoid cavity
|
|
Glenoid cavity is lined by cartilaginous _____
|
Glenoid labrum (make the cavity more "cup shaped"
|
|
What is the radius and what are the major components o itf?
|
Radius is the lateral forearm bone--thumb sideComponents include the head (capitulum), radial tuberosity, and styloid process.
|
|
What is the ulna? and what are components found in the ulna?
|
Ulna is a medial forearm bone-->pinky sideContains:- the trochlear notch (which serves as articulation point with trochlea of humerus)-olecranon process (which goes in the olecronon fossa)-Coronoid process (which goes in the coronoid fossa)-styloid process
|
|
Radius can freely rotate along the ____(pivot joint) to allow for _____ and _____ of the forearm
|
1. capitulum2. pronation3. supination
|



