Cards In This Set
| Front | Back |
|
What are the 2 major formations
|
Arctic tundra and alpine (high elevation) tundra
|
|
Where is this biome located
|
N-hemi= fringe of arctic ocean
S-hemi= southern South America, fringe of Antarctica high elevations, above altitudinal treeline |
|
What is the climate like?
|
Temperature: summer: short season, w/ long days, t>0 (24hrs daylight)
winters: long avg. T<<0 (long periods of darkness) high annual range; low daily range ppt: low= "arctic desert" summer (wetter), winter snow + wind humidity: -both ppt + evaporation=low=relative humidity is high water balance: primarily E limited = Low PE -small H2O deficit in summer |
|
Draw the soil moisture water balance
|
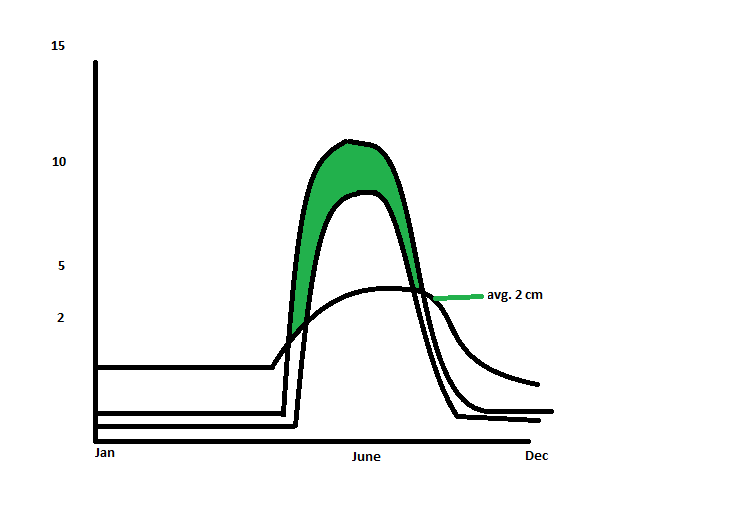 See graph |
|
Types of soils?
|
Permafrost: ground permanently frozen
- true arctic defined by this -sub= patches of frozen Active layer: surface that thaws in summer -usable for plants + substrates |
|
What is the soil water paradox
|
-permafrost prevents H2O from percolating into soil + flat landscape + surface runoff= lots of standing H2O
this is why tundra is humid even though there is little ppt |
|
What are the vegetation characteristics
|
Barren land
life forms= bryophytes, herbs and shrubs limited by: -cold temperatures -short growing season -cant get deep roots b/c permafrost |
|
What are the plant adaptations
|
Will grow shallow roots
dwarf growth form: due to wind + ice will grow smaller drought resistance: soil H2O frozen -have to be accustomed to little water 99% perennial: growing season too short for annuals -quickly rebuild regenerative sources abundant root vs shoot biomass:storage organs are below ground and there are more for ex) the arctic heather will put new green material where plant left off |
|
What are the disturbances
|
Freeze-thaw action of soil
-results in variable moisture conditions in space and time -frost heaving -sorts-soil particles by size |
|
Why is energy so low?
|
Low annual insolation and intensity is low
extreme seasonality high reflection H2O takes energy to melt |
|
What is thermokarst?
|
A human impact: H2O expands + forces soil up
-when volume decreases soil creates pattern ground hummocky topography, where irregular pits and depressions develop |
|
What is another human impact?
|
Driving which deepens the active layer causing melting of soil which decrease volume of soil, results in depressions which fill with water, melts more, subsides more mechanical disturbance.
resource extraction consequences: variable moisture conditions in space + time (flooding, inundations, + drought) |
|
Why is the arctic warm faster?
|
1 darker land: absorbs more slaor E
2 more of the xtra trapped E goes diectly into warming rather than into evap 3 the atmosphere layer that has to warm in order to war the surface is shallower in the arctic 4 as sea ice retreats solar heat absorbed by the oceans is easily transferred to atmosphere 5 alterations in atmosphere and oceanic circulation can increase warming -equatorial water moves to moles |
|
What are the effects of climate change?
|
Decrease sea ice and snow
vegetation will increase because more sun. |



