Cards In This Set
| Front | Back |
|
|
Simple Squarmous.
Thin single cell layer
where the width is
greater than the cell’s
height.
|
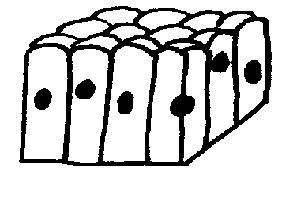 |
Cubodial epithelium.
Thin single cell layer
where the width,
depth, and height of
the cell are
approximately the
same
|
 |
Stratified squamous.
Multiple layers of
cells but the top layer
is squamous
Keratinized – layer of
dead apical cells
Non-keratinized –
layer of living apical
cells.
|
|
What is the function of muscular tissue?
|
Provide stability to the skeleton and internal organs.
Allows body movement.
|
|
Where is Cardiac muscle found?
|
In the heart.
They are branched striated branched muscle.
Cells are joined togetehr by disks which allow synchronisation of the heart beat.
|
|
What are the three types of muscle tissue?
|
Cardiac- Heart
Skeletal- attached to bone
Smooth- walls of blood vessels in digestive system, respiratory & the eye.
|
|
What are membranes composed of?
What are the main types?
|
Composed of epithelial & connective tissue.
Main types:
Epithelial
Muccous
Sevous
Synovial
|
|
Where do yuo find glial tissue?
|
In the nervous Tissue
|
|
What is the difference between endocrine and exocrine glands.
|
Endocrine secretes directly into the bloodstream (hormone)
Exocrine secretes into a duct. Salivary mammary , liver and pancreas.
|
|
What are the two types of tissue found in the Nervous system?
|
Excitable- Called neurones & they initiate recieve conduct & transmit info.
Non- Excitable (glial)- Support the Neurones.
|
|
Where are loose (areolar connective tissue found and what does it do?
|
Found in almost every part of the body.
Provides elasticity and tensile strength.
eg; under the skin
Between the muscle
Supporting blood vesses& nerves
in glands supporing secretory cells
|
|
Where can Fibrous tissue be found
|
Forming ligamnets
Periosteum- outer protective layer for bone
forming muscle sheaths
Protective layer for some organs
eg- Brain
-kidney
-lymph nodes
|
|
What are the 4 major types of tissues?
|
Nervous
Connective
Epithelial
Nervous
|
|
Why do some tissues have cilia present?
Give and example
|
Cilia are finger like projections from the cell that aid in trransportation of the cells or moving liduid over their surface
eg:
lungs
follopian tubes
Vesicles of the brain
|
|
What are some cells in the connective tissue?
|
Fibroblasts
Fat cells
Macrophages
Leukocytes
Plasma Cells
Mast Cells
|



