Cards In This Set
| Front | Back |
|
Location of the heart
|
Midiastinum between the second and fifth intercostal space
Superior surface of daiphragm Two thirds to the left of the midsternal line Anterior ro the vertebral column, posterior to sternum |
|
Where is heart enclosed
|
Pericardium, doubble walled sac
|
|
Location of heart (picture)
|
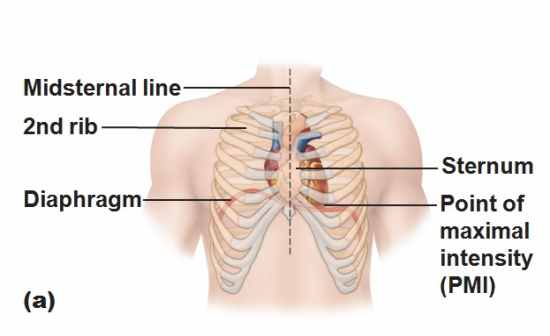 |
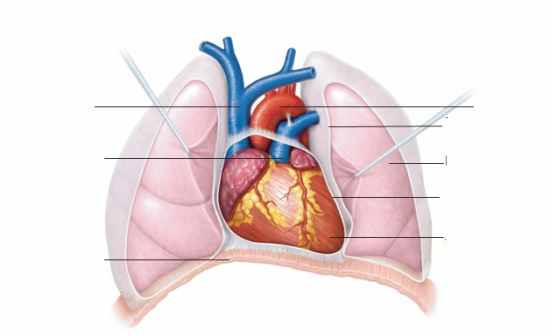 |
Superior vena cava
Pulmonary trunk Diaphragm Aorta Parietal pleural Left lung Pericardium(cut) Apex of heart |
|
What does the superficial fibrous pericardium do?
|
Protects, anchors, and prevents overfilling
|
|
What are the two layers of the deep two layered serous pericardium?
|
Parietal
Visceral |
|
Parietal layer of pericardium
|
Lines the internal surface of fibrous pericardium (belonging to walls)
|
|
Visceral layer of pericardium
|
External surface of organ (belonging to organ)
|
|
Pericarditis
|
Inflammation of the pericardium - roughens serous membrane surface. Patients complain of pain deep in the sternum.
|
|
Cardia tamponade
|
When the peicardial cavity is overfilled
|
|
Epicardium
|
Visceral layer of the serous pericardium
|
|
Myocardium
|
Spiral bundles of cardiac muscle cells
Fibrous skeleton of the heart: crisscrossing, interlacing layer of connective tissue |
|
Myocardium function
|
Anchors cardiac muscle fibers,
Supports great vessels and valves, Limits spread of action potentials to specific paths |
|
Endocardium
|
Continous with endothelial lining of blood vessels
|
|
The cardiac muscle bundles prevent what?
|
Stretching of the valves and vessels
|



