Related Topics
Cards In This Set
| Front | Back |
|
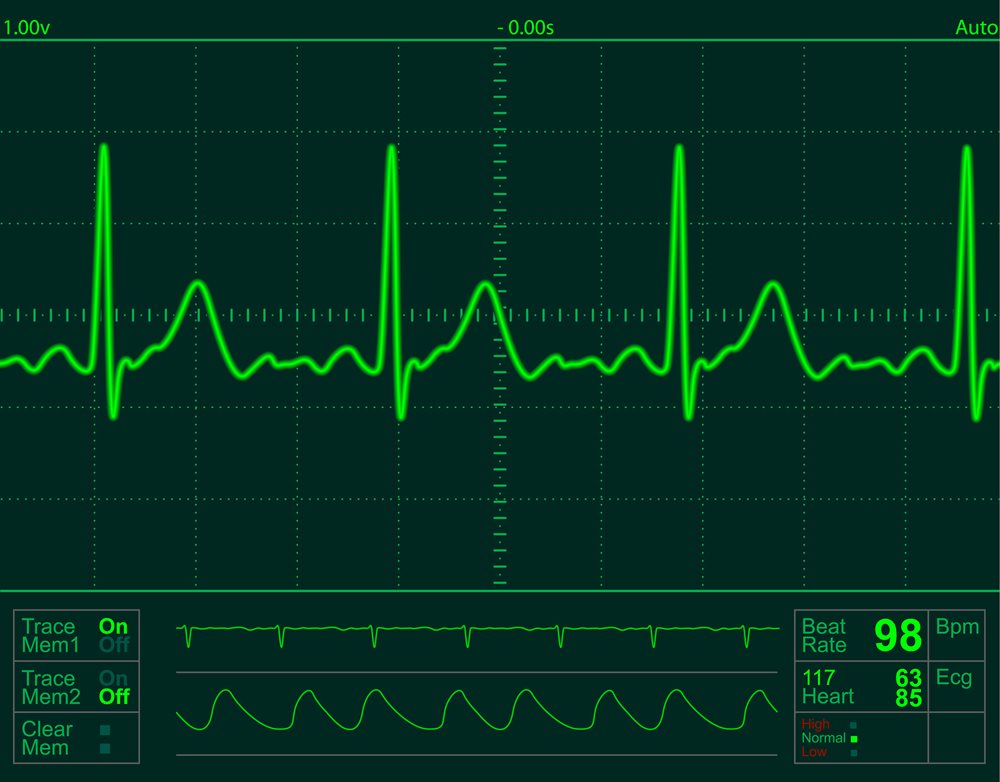
An electrocardiogram is a/an?
|
Graphic record of the heart's electrical activity
|
|
The electrocardiograph can be used except?
|
Determine cardiac output
|
|
_____ positioned on the patient's skin detect the heart's electrical activity.
|
Electrodes
|
|
Impulses that travel toward a positive electrode and away from a negative electrode are recorded on the electrocardiogram as _____ deflections.
|
Upward
|
|
The lead most commonly used for continuous cardiac monitoring is lead?
|
Lead II
|
|
With lead II, the ____ lead wire is the positive electrode.
|
LL - left leg
|
|
Bipolar leads?
|
Require two electrodes of opposite polarity
|
|
The frontal plane gives us a/an _____ view of the heart's electrical activity.
|
Anterior and posterior
|
|
The limb leads are obtained by placing electrodes on the?
|
Right arm, left arm, left leg, and right leg
|
|
An EKG printout?
|
Provides a more accurate picture of the ST segments than does the oscilloscope
|
|
Each small square on the EKG paper running horizontally represents seconds in duration?
|
0.04 seconds
|
|
The larger box on the EKG paper, made up of five small square, represents _____ seconds in duration.
|
0.20 seconds
|
|
On the top or bottom of the EKG paper there may be vertical slashes or markings to represent _____ second intervals.
|
3
|
|
Each small square on the EKG paper running vertically represents?
|
0.1 mV.
|
|
The reference point used to identify the changing electrical amplitude on the EKG is called?
|
Isoelectric line
|