Cards In This Set
| Front | Back |
|
Peripheral Nervous System (PNS)
|
-Nervous system outsid the brain and spinal cord
-provides vital links to the body and outside world -nerves allow the CNS to receive info and intitae action |
|
Sensory receptors
|
Pick up stiumul from inside or outside the body
|
|
Nerves
|
Bundles of axons
|
|
Ganglia
|
Clusters of peripheral neuronal cell bodies
|
|
Motor endings
|
Aon terminals of motor neurons
-> innervate effectors (muscle fibers and glands) |
|
Somatic body region
|
Structures external to the ventral body cavit(ex: outer tube) skin, skeletal musculature, axial bones, and appendiucular bones and musscles
|
|
Visceral body region
|
Contains viscera within the ventral body cavity (ex:inner tube- digestive tube, lungs, heart, spleen, bladder, etc) as well as smooth muscle and glands throughout the body
|
|
Somatic sensory
|
Sensory innervation of outer tube (skin, trunk wall) and limbs
|
|
Visceral sensory
|
Sensory innervation of viscera
|
|
Somatic motor (voluntary motor)
|
Motor innervation of skeletal muscles of outer tube & limbs
|
|
Visceral motor (autonomic nervous system)
|
Involuntary motor innervation of the inner tube (smooth muscle, cardiac muscle, glands) some outer tube structures (arrector pilli muscles and sweat glands) and smooth muscle in blood vessels
|
|
Image of functional Organization of PNS
|
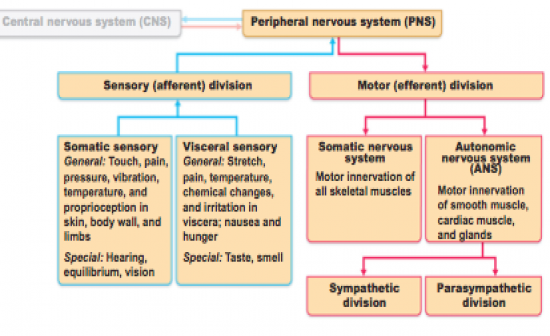 |
|
Somatic Division of the nervous system
|
-general somatic senese
-proprioceptive senses -special somatic senses |
|
General somatic sensory divison
|
-touch
-pain -vibration -pressure -temperature |
|
Proprioceptive senses of somatic sensory division
|
-detect stretch in tendons, joint capsules and muscles
-body sense: position and movement of body in space |



