Related Flashcards
Cards In This Set
| Front | Back |
|
Normal respiratory rate is
|
30 to 60 breaths per minute
|
|
How long should you count for respiratory
|
A full min
|
|
What is a new born respirations like?
|
Quiet and shallow with short periods of apnea (less than 15 seconds).
Breathes with diaphram
|
|
What is a diaphragmatic hernia
|
An opening in the diaphragm which creates an opening between the thoracic and abdominal cavities. This allows abdominal contents, such as loops of intestine, etc. to push into the thoracic cavity, displace the heart and create breathing difficulties for the neonate. The displaced structures will also alter the shape of the chest, resulting in asymmetry.
|
|
What is a pneumothorax
|
Accumulation of air in the pleural space which prevents the lung tissure from expanding properly. The lay term for pneumothorax is "collapsed lung"
|
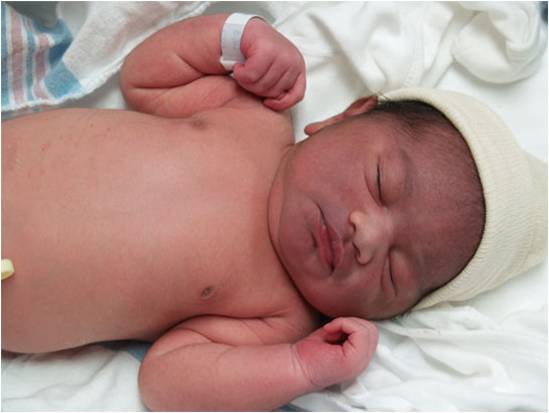 What has happend to the baby, how can you tell by the picture? |
A baby born vaginally with a face presentation
Evidence: marked bruising or petechiae on the face
|
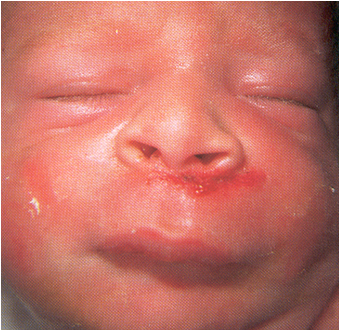 What has happend to the baby, how can you tell by the picture? |
A baby born vaginally with a face presentation
Evidence: Facial trauma, and bruising
|
 What has happend to the baby, how can you tell by the picture? |
A baby in the breech position may exhibit a posture other than flexed or may have bruised, edematous parts of the lower body
|
|
Types of delivery? And what do they present with?
|
A baby born via vaginal delivery with the vertex presenting is likely to exhibit molding of the head.
A baby born vaginally via forceps may exhibit forceps marks.
A baby born vaginally via vacuum extraction may exhibit swelling under the scalp.
A baby born via C-section is frequently more prone to respiratory distress and should be observed closely.
|



