Cards In This Set
| Front | Back |
 What is the Visible Perception Spectrum? |
The range of wavelengths of light to which the human eye is sensitive. Starts at short wavelengths of 380 which we perceive as purple and violet. Longer wavelengths produce blue, green, yellow and orange perceptions until we reach red, which has a wavelength of 750 nanometres.
|
|
What is electromagnetic energy?
|
Light waves that exist in the external environment, including X-rays, radio waves and light waves.
|
|
What is hue?
|
Hue is the perceptual quality of light that we call colour.
|
|
What is brightness?
|
The physical amplitude, or height, of light waves; therefore amplitude determines the perceived brightness of a light.
Waves of greater amplitude are "taller", carry more energy and cause colours to appear brighter or more intense. Waves of lower amplitude are "shorter" carry less energy, and cause colours to appear duller or less intense. |
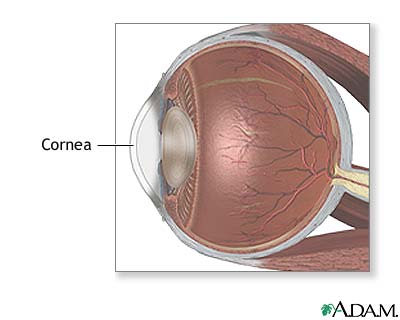 What is the cornea? |
The cornea is a transparent, convex-shaped membrane that protects the front part of the eye.
|
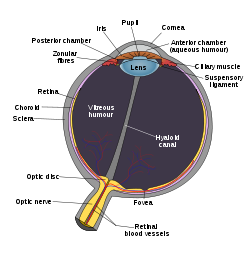 What is the pupil? |
The pupil is an adjustable opening in the centre of the eye's iris through which light enters, appears as black.
|
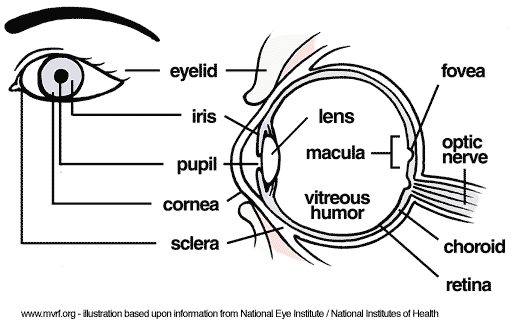 What is the iris? |
The iris is a coloured, circular muscle inside the eye that expands and contracts to change the size of the pupil.
|
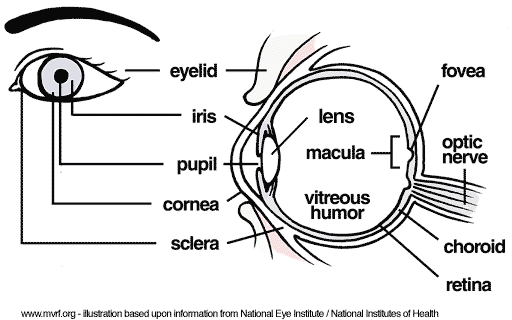 What is the lens? |
The lens is a transparent, convex structure behind the iris that changes shape to focus light into an image on the retina.
|
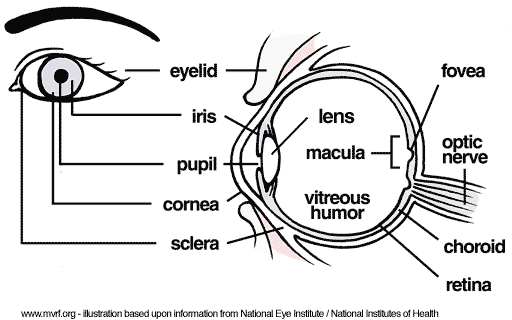 What is the retina? |
The retina is a light-sensitive membrane composed of a number of layers of specialised neurons at the back of the eye.
|
|
What are the photoreceptors?
|
Receptor cells located at the back of the retina and specialised to detect and respond to light. Rods and Cones.
|
|
What are the cones?
|
The cones are a group of photoreceptors, located mainly in the centre of the retina, specialised to detect and respond to bright light and responsible for day vision, colour vision and visual activity.
|
|
What are the rods?
|
The rods are a group of photoreceptors located mainly in the outer ends of the retina specialised to detect and respond to dim light and responsible for night vision, black and white vision and peripheral vision.
|
|
What are the processes of sensation?
|
- Reception- Transduction- Transmission
|
|
What is Reception?
|
Reception is the process of sensory receptors detecting the presence of a stimulus or changes to a stimulus (in visual perception, when the light stimulus is focused on the retina and detected by photoreceptors)
|
|
What is Transduction?
|
Transduction is the process of sensory receptors converting stimulus energy into impulses of electrochemical energy for neural activity (When photoreceptors convert light into coded impulses of electrochemical energy)
|



