Cards In This Set
| Front | Back |
|
Name the phylum
|
Phylum Diplomonadida- 2 nuclei, mult flagella (Giardia lamblia)
|
 Name the phylum |
Phylum Parabasala trichimonads (Trichimonas vaginalis) - STD; large modified golgi, mult flagella
|
 Name the phylum |
Phylum Euglenozoa subphylum euglenophyta- flagella, mixotrophic, metaboly
|
|
Name the phylum
|
Phylum Euglenozoa Subphylum kinetoplastida- kinetoplast houses DNA (Trypanosoma)- sleeping sickness
|
|
Name the phylum
|
Superphylum Alveolata, Phylum Dinoflagellata- rigid armor appearance; red tide; symbiotic with clams
|
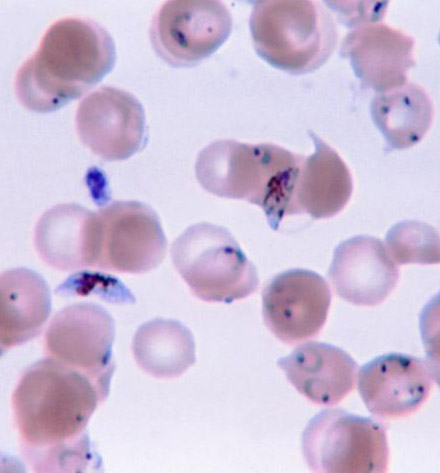 Name the phylum |
Alveolata Phylum Apicomplexa-(Plasmodium):Apical complex for penetration of host, cause of malaria
|
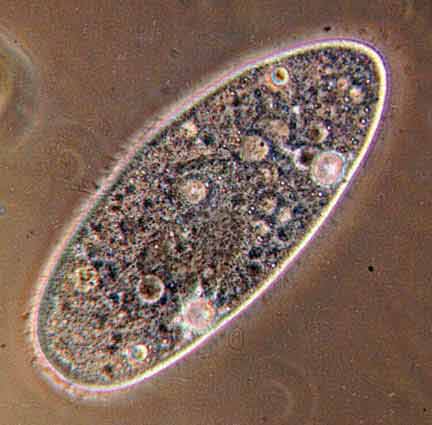 Name the phylum |
Alveolata Phylum Ciliophora: macronucleus; paramecium
|
 Name the phylum |
Stramenopila Phylum Oomycota; water molds; originally classified as fungi; white rust on leaves, white hair on fish
|
 Name the phylum |
Phylum Bacillariophyta - diatoms; brown alive shell remains when dead; slimy feeling of rocks and plants from lipids
|
 Name the phylum |
Phylum Phaeophyta Brown algae; kelp; have root like system called holdfast, blade (leaf) and stipe (stem) also a gas bladder
|
 Name the phylum |
Phylum Foraminifera - Forams; contain porous shells and use pseudopodia to move; mostly known from fossil record
|
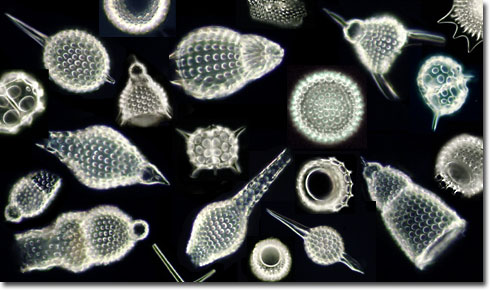 Name the phylum |
Phylum Actinopoda -Radiolarians; ray-like pseudopodia; some fossils (rad. ooze) can be over 100 meters thick
|
 Name the phylum |
Phylum Rhodophyta red algae; usually red, branched and lacy body form, lack of structure
|
 Name the phylum |
Chlorophyta Green algae; always green use chlorophyll; close relative to plants; sea lettuce, volvox, spirogyra
|
|
Name the phylum
|
Chlorophyta Green algae; always green use chlorophyll; close relative to plants; sea lettuce, volvox, spirogyra
|



