Cards In This Set
| Front | Back |
|
What are the two groups of angiosperms?
|
Monocots and diocots (eudicots)
monocots - embryo has one seed leaf
diocots - embryo has two seed leaves
|
|
What is a plant organ?
|
Consiss of sevelal types of tissues that together carry out particular functions.
|
|
On behalf of the plants, its stem and leaves will be depended on what sources from generalized environment.
|
They will be depended on water and minerals absorbed by roomts in order to develop, reproduce, and structure.
|
|
Define root system
|
A plant's ________anchors it in the soil, absorbs and transports minerals and water, and stores food.
-The fibrous root system of a monocot consists of a mat of generally thin roots spread out shallowly in the soil
-eudioctos have one main vertical taproot with many small secondary lateral roots growing outward.
|
|
ROOT HAIRS
|
The root in both monocots and eudicots, a vast number of tiny projections called _______.
________ - enormously increase the root surface area for absorption of water and minerals.
|
|
SHOOT SYSTEMS
|
A plant is made up of stems, leaves, and adaptations for reproduction - flower, in angiosperms.
Sterms: are generally above ground, supported leaves and flowers.
|
|
NODES, INTERNODES, NODES
|
A stem has _____, the points at which elaves are attached, and ________, the portions of the stem betwee ________.
|
|
DEFINE: LEAVES
|
Are the main photosynthetic organs in most plants although green stems also perform photosynthesis. Most leaves consist of a flattened blade and a stalk, or petiole, which joins the leaf to a node of the stem.
|
|
Define: TERMINAL BUD, AXILLARY BUDS
APICAL DOMINANCE
|
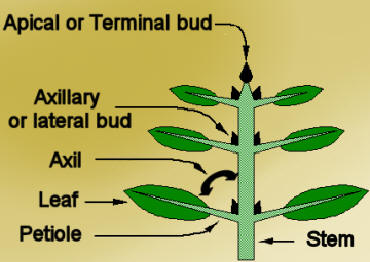 1. at the apex (tip) of the stem, has developing leaves and a compact series of nodes and internodes. called __________. 2. one in the each of the angles formed by a leaf and the stem, are usually dormant. called _____. 3. In many plants, the terminal bud produces hormones that inhibit growth of the axillary buds, a phenomenon called ___________. |
|
What happen to the plant when removing the terminal bud?
|
Usually stimulates the growth of axillary buds. THi is why pruning fruits trees and "pinching back" houseplants makes them bushier.
|
|
Name the two organ systems and three basic organs found in all plants.
|
ROOT SYSTEMS and SHOOT SYSTEMS
Roots, stems and leaves
|
|
Name several plants that all are ususally formed large taproots that store food in the form of carbohyrates such as starch.
|
Carrots
Turnips,
Sugar beets, and sweet potatoes
|
|
DEFINE: RHIZOMES
|
 -the large, brownish, rootlike structures. -horizontal stems that grow just below or along the soil surface -store food and, having buds, they can also spread and form new plants. |
|
DEFINE: TUBERS
|
 The potato plant has rhizomes that end in enlarge structures specialized for storage called ______. (the potatoes we eat) |
|
DEFINE: Tendril
|
A modified leaf with its tips coiled around a stem. ____ help plants climb
-find in grapevines are known as modified leaves that protect the plant from being eaten by animals.
|



