Cards In This Set
| Front | Back |
|
Alpha Decay
|
A nuclear reaction in which an
 particle ( particle (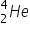 ) is emitted: ) is emitted: 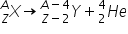 |
|
Gamma Decay
|
A nuclear reaction in which high-energy photons, also known as y-particles, are emitted:
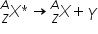 |
|
Capacitor
|
An electric device used in circuits that is composed of two conducting plates separated by a short distance; these devices store electric charge.
|
|
Mass
|
A scalar quantity used as a measure of an object's inertia.
|
|
Ohm's Law
|
Law stating that the voltage drop across a resistor is proportional to the current flowing through it, given by the equation V=IR.
|
|
Wave Speed
|
The speed of a wave, which is related to its frequency and wavelength by the equation
 . . |
|
Displacement
|
A vector quantity describing the straight-line distance between an initial and a final position of some particle or object.
|
|
Electromagnetic Waves
|
When an electric field is changing, it causes a change in a magnetic field and vice-versa, resulting in the propagation of a wave containing an electric and a magnetic field that are perpendicular to each other.
|
|
Exponential Decay
|
A decrease in the amount of substance N at an exponential rate. Given by the equation:
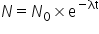 |
|
Current
|
A flow of charge per time. The flow of charge is motivated by a potential difference (voltage). Current is denoted I and can be calculated as
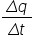 . Current is conventionally considered the theoretical movement of positive charge. . Current is conventionally considered the theoretical movement of positive charge. |
|
Electric Circuit
|
A conducting pathway that contains one or more voltage sources that drive an electric current along that pathway and through connected passive circuit elements (such as resistors).
|
|
Elastic Potential Energy
|
The energy associated with stretching or compressing a spring, calculated by the equation
 and given in the SI unit of joules (J). and given in the SI unit of joules (J). |
|
Potential Difference
|
The difference in electric potential between two points in an electric field, also called the voltage (
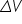 ). ). |
|
Center of Mass
|
The point of some object or body where all of its mass is considered to be concentrated. In a uniform gravitational field, this is also the center of gravity.
|
|
Half-Life
|
The amount of time it takes for one-half of a radioactive sample to decay, given by the equation
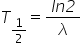 , where , where 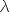 is a decay constant. is a decay constant. |



