Cards In This Set
| Front | Back |
|
8.1.1
State that thermal energy
may be completely converted to work in a single process, but that continuous
conversion of this energy into work requires a cyclical process and the
transfer of some energy from the system
|
Thermal energy may be
completely converted to work in a single process, but continuous conversion of
this energy into work requires a cyclical process and the transfer of some
energy from the system
|
|
8.1.2
Explain what is meant by degraded
energy
|
Energy no longer available
to perform useful work, usually lost to surroundings and other processes
|
|
8.1.3
Construct and analyse
energy flow diagrams (Sankey diagrams) and identify where the energy is
degraded
|
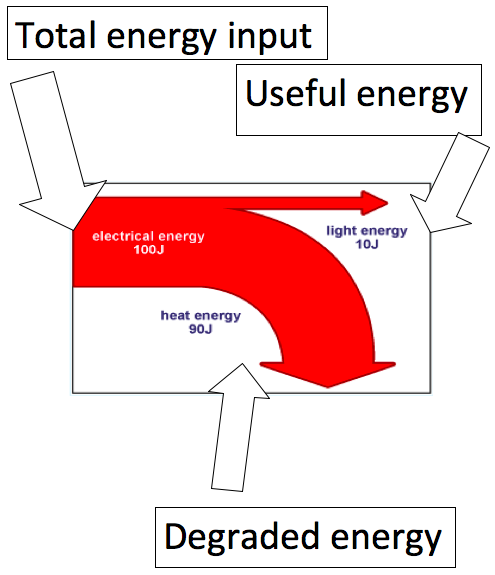 Refer to image |
|
Outline the principal
mechanisms involved in the production of electrical power
|
1. Any force that
will spin a turbine (e.g. steam from water heated by burning fossil fuels,
wind, waves, etc.)
2. Turbine causes
generator to produce electricity from electromagnetic induction
|
|
8.2.1
Identify different world
energy sources
|
1. Coal
2. Oil
3. Natural gas
4. Nuclear
5. Solar
6. Wind
7. Wave
8. Tidal
9. Hydroelectric
10. Geothermal
|
|
8.2.2
Outline and distinguish between
renewable and non-renewable energy sources.
|
Renewable
– may be replaced as quickly as it is consumed
Non-renewable
– may not be replaced as quickly as it is consumed
|
|
8.2.3
Define the energy density
of a fuel
|
Energy density of a fuel –
amount of chemical energy stored per unit mass/volume of a fuel
|
|
8.2.4
Discuss how choice of fuel
is influenced by its energy density
|
Greater energy density = greater
energy per unit mass/volume = more energy for same mass/volume = more efficient
|
|
8.2.5
State the relative
proportions of world use of the different energy sources that are available
|
 Refer to image |
|
8.2.6
Discuss the relative
advantages and disadvantages of various energy sources
|
 Refer to image |
|
8.3.1
Outline the historical and
geographical reasons for the widespread use of fossil fuels
|
Historical
-Industrial Revolution had large energy
demands
-Household appliances and heavy industrial
machinery require large amounts of energy
Geographical
-Fossil fuel reserves abundant in most
continents
-Industrial developments
centered around fossil fuel deposits
|
|
8.3.2
Discuss the energy density
of fossil fuels with respect to the demands of power stations
|
Refer to image
|
|
8.3.3
Discuss the relative advantages and
disadvantages associated w/ the transportation & storage of fossil fuels.
|
Coal
Advantages
-simple storage
-safe
Disadvantages
-low energy density
Oil
Advantages
-convenient location of rigs
Disadvantages
-oil spills and leaks
-vulnerable to terrorist activities
and natural disasters
Natural gas
Advantages
-high energy density
Disadvantages
-expensive gas line setup and
maintenance costs
|
|
8.3.4
State the overall
efficiency of power stations fuelled by different fossil fuels
|
Coal - 35%
Oil – 38%
Natural gas – 45%
|
|
8.3.5
Describe the environmental
problems associated with the recovery of fossil fuels and their use in power
stations
|
Coal
Recovery
-strip
mining (sulfuric acid and soil erosion)
-mining
hazards (toxic gas and tunnel cave ins)
Oil
and Natural gas
Recovery
-extensive
time to map and plan construction
-expensive
construction and maintenance costs
-possible
spill and leak risks
Power
Station Use
-air pollution (CO2,
CO, SO2, soot, Nitrogen oxides emissions)
|



