Cards In This Set
| Front | Back |
 This comes from a patient who has stomach pain after taking a bottle of Advil and a fifth of vodka. What is this? |
Acute gastritis
|
|
Name 3 categories (and examples) of etiologies of chronic gastritis
|
Chronic infection: H. pylori
Autoimmune: Assoc. w/ pernicious anemia Toxic: Alcohol, smoking |
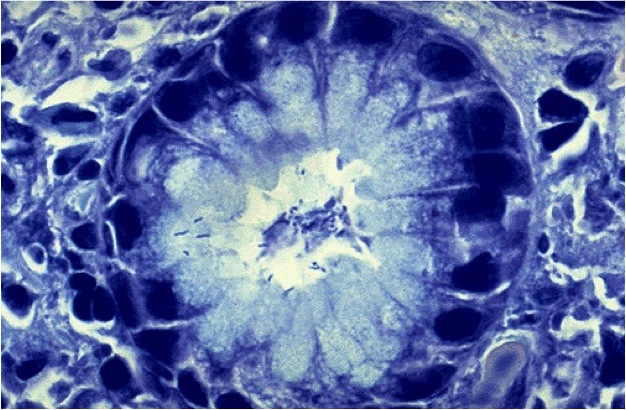 What is the organism seen here? |
H. pylori
|
|
Name 5 conditions associated with H. pylori
|
Chronic gastritis
gastric ulcers duodenal ulcers MALT lymphoma Adenocarcinoma |
|
What are the two 1st line drugs to treat H. pylori?
Which is preferred when resistance is not a factor? What is second line? |
 Clarithromycin and metronidazole Clarithromycin is used unless resistance is >15% Whichever of the two 1st line drugs you haven't tried yet |
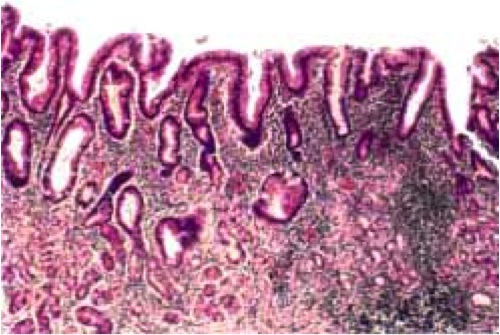 What is this? |
Chronic gastritis
|
|
Which cells and regions of the stomach are affected in autoimmune chronic gastritis?
|
Parietal cells
Body and fundus (b/c that is where parietal cells are) |
|
Name at least 3 things different in environmental chronic gastritis compared to autoimmune
|
Affects the antrum as well as the body
decreased G cells --> low gastrin and hypochlorhydria not associated with antibodies or pernicious anemia It is associated with ulceration (auto is not) |
|
What is the difference between reactive gastropathy and gastritis?
|
There is hemorrhage but minimal inflammation in reactive gastropathy (causes are similar)
|
|
What are the most common sites of peptic ulcers?
|
(In order from most to least common)
Duodenum, first portion Stomach (antrum) GE junction (reflux, Barrett's) Within margins of a gastrojejunostomy In the duodenum, stomach, and/or jejunum in Z-E syndrome Within or next to an ileal Meckel diverticulum that contains ectopic gastric mucosa |
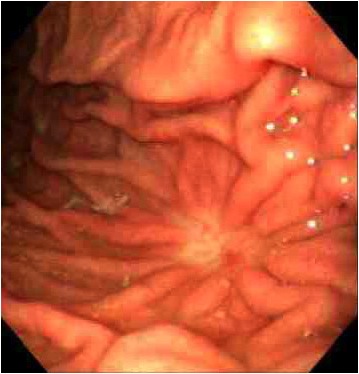 What is this? |
Peptic Ulcer
|
|
What blood type is associated with an increased risk of H. pylori infections and resultant diseases?
|
Type O
|
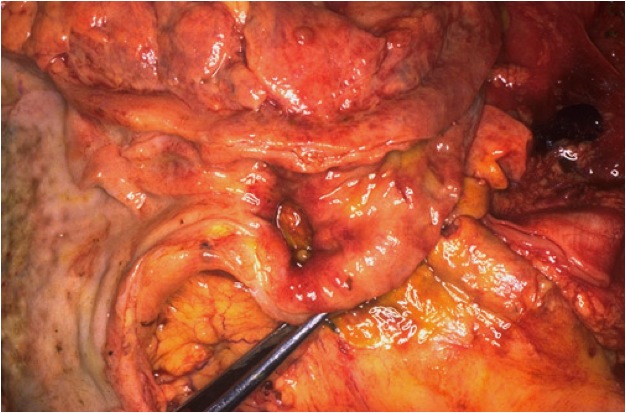 What is shown in the center of this image just above the forceps? |
Penetrating acute duodenal ulcer
|
|
What causes Zollinger-Ellison syndrome?
|
Pancreatic or duodenal tumor causes hypergastrinemia, resulting in extremely high acid production. This leads to multiple ulcers (rather than the usual solitary ulcer) that are usually unresponsive to therapy.
|



