Cards In This Set
| Front | Back |
|
Alkane
|
 a saturated hydrocarbon, consists only of hydrogen and carbon atoms, All bonds are single bonds, They have the general formula CnH2n+2, when naming use suffix -ane |
|
Alkene
|
 An unsaturated hydrocarbon, contains a double bond between two carbons, they have the general formula CnH2n, when naming use suffix -ene |
|
Alkyne
|
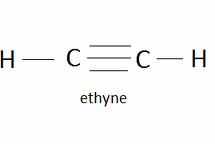 Triple bond between two carbon atoms, they have the general formula CnH2n- 2, when naming use suffix -yne, an unsaturated hydrocarbon |
|
Cyclic (ring) structures
|
 Hydrocarbons in which the 2 ends of the chain are attached at the ends to form a ring They are either saturated or unsaturated cyclic hydrocarbons |
|
Alcohols
|
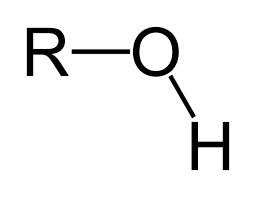 Belongs to the hydroxyl functional group, contains an oxygen and hydrogen, represented as -OH ( or HO-) within a molecule, when naming use suffix -ol |
|
Aldehydes
|
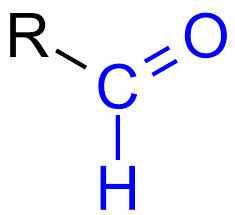 Belongs to the carbonyl functional group, contains a carbon double bonded to an oxygen and singly bonded to a hydrogen |
|
Ketones
|
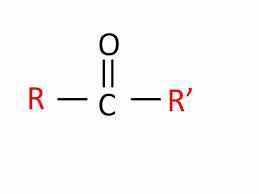 Belongs to the carbonyl functional group, contains a carbon double bonded to an oxygen |
|
Ethers
|
 Belongs to the alkoxy functional group, an oxygen between two carbons |
|
Esters
|
 Consists of a carbonyl functional group (C=O) adjacent to an ether linkage (oxygen between 2 carbons). |
|
Alkyl halides
|
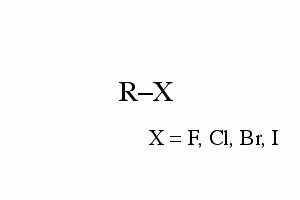 The R in the general form is typically an alkyl group (chain of carbons) with a halogen replacing one of the hydrogens. |
|
Hydrocarbons (2 types)
|
Hydrocarbons are organic compounds made up of only the elements carbon and hydrogen. Two types are saturated and unsaturated,
|
|
Saturated hydrocarbons
|
Saturated means that the hydrocarbon has only single bonds and that the hydrocarbon contains the maximum number of hydrogen atoms for each carbon atom.
|
|
Unsaturated hydrocarbons
|
Unsaturated means that the hydrocarbon contains one or more double or triple bonds.
|
|
Organic chemistry
|
The study of organic compounds that contains mainly carbon atoms
|
|
Organic compounds
|
contain carbon and hydrogen, often combined with a few other elements.
|



