Cards In This Set
| Front | Back |
|
Cyst Definition
|
- an abnormal cavity, lined by epithelium, containing fluid or semi-solid material
- can be developmental and get larger in time can be found in soft tissue as well as bone |
|
Cyst Classification
|
- based on the source of the epithelium (odontogenic cyst, non-odontogenic cyst)
- based on their location (soft tissue, intrabony) |
|
Odontogenic Cyst
|
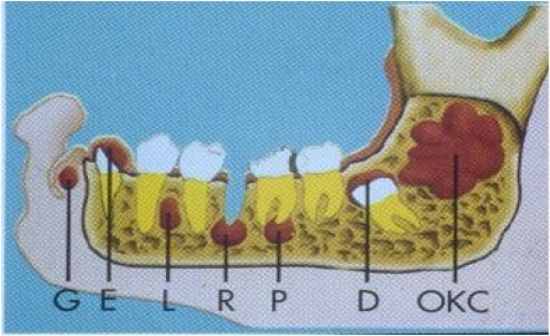 - a cyst which the lining of the lumen is derived from epithelium produced during tooth development - can come from different parts of the odontogenic structures (Rests of Malassez, reduced enamel epithelium, dental lamina, etc) - Also Classified on their location |
|
Periapical Cyst Definition
|
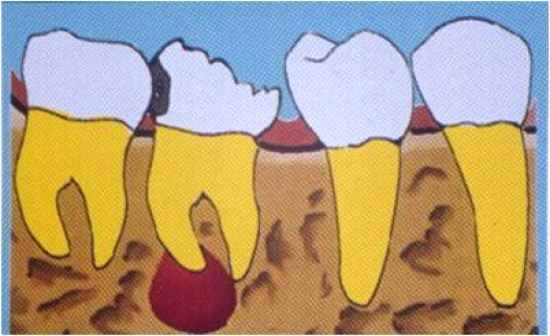 - odontogenic cyst from the Rests of Malassez, this is one of the most common cysts - located at the root apex of the tooth - the tooth must be infected or inflammed which will extend to the apical area - an odontogenic cyst of inflammatory origin that is preceeded by a chronic PA granuloma and stimulation of rests of Malassez |
|
Periapical Cyst Characteristics
|
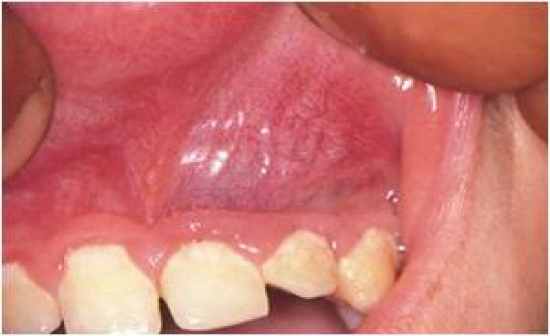 - PA cyst is always a radiolucency, but we cannot make a diagnosis based on the radiograph alone - we cannot determine a cyst from a chronic inflammation (apical granuloma) without histological evaluation - Failed RCT will lead to a PA cyst - one requirement is having a necrotic/infected tooth (if the tooth is intact, this will be some other pathology) |
|
Periapical Cyst Treatment
|
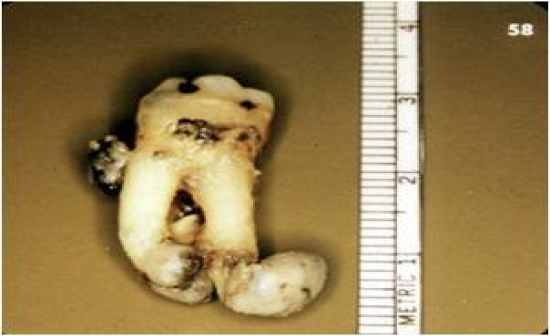 - apical surgery is necessary to remove the cyst and then retrofill the lesion - if the tooth is not salvagable, then we must remove the retained root and remove the cyst otherwise it will turn into a residual cyst - note that histologically there are inflammatory cells and a capsule surrounding an epithelial layer with a lumen on the interior |
|
Rushton Bodies
|
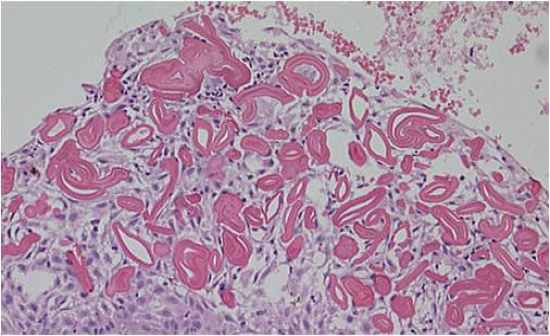 - these are eiosinophilic bodie which result from degenerative changes in cells in some (not all) of the cystic lesions - this is an indication of the longevity of a chronic lesion |
|
Residual Cyst
|
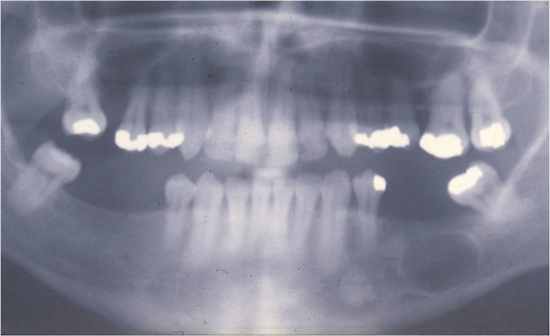 - this develops from an untreated radicular cyst - we must curate the lesion otherwise it will lead to a residual cyst |
|
Dentigerous Cyst (Follicular Cyst)
|
 - this is an odontogenic cys (from the developmental structures of the tooth) which surrounds the crown of an impacted tooth - caused by fluid accumulation between the reduced enamel epithelium and enamel surface resulting in a cyst - this is a pericoronal cyst of an impacted tooth - lined by non-keratinized epithelium (could be inflammed or not) |
|
Eruption Cyst
|
 - this is an odontogenic cyst with the histologic features of a dentigerous cyst that surrounds a tooth's crown that has erupted through the bone but NOT the soft tissue - clinically is visible as a soft fluctuant mass on the alveolar ridges - found in children who are in the process of erupting their teeth - possible to have a blue-ish color due to trauma and bleeding with pigments (hemosiderin) |
|
Odontogenic Keratocyst (OKC)
|
- cyst derived from the remnants, rests of the dental lamina with a biologic behavior similar to a benign neoplasm
- distinct lining of 6-10 cells in thickness that exhibits a basal cell layer of palisaded cells and a surface of corrugated parakeratin - they can be found anywhere in the mouth, when around the root of a tooth they can cause resorption of the bone |
|
Odontogenic Keratocyst Characteristics
|
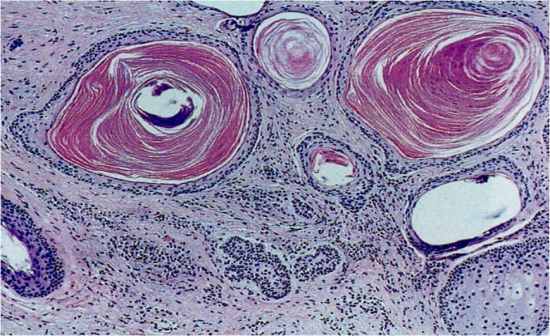 - this has histologically keratinized epithelium, thus if you look at the lumen of the OKC it will be filled with a cheezy material (keratin) - have a uniform thickness with a flat basal membrane, no rete pegs, and a 7-8 cell layer - not usually inflamed, not irritated - also might see a micro-cyst or a daughter/satellite cyst in the cell wall of the OKC (leading to an increased probability of recurrence |
|
OKC in Basal Cell Carcinoma Syndrome
|
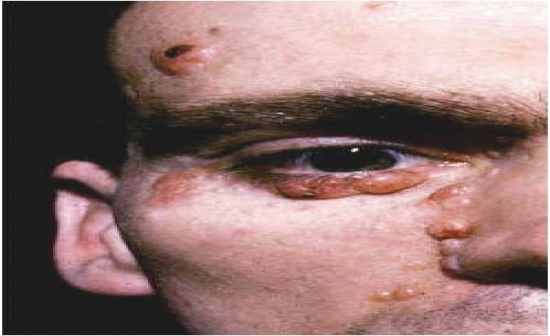 - most of the OKC are single and thus if there are multiple present we must think of BCC syndrome - also present with bifid ribs, pitting of the skin, CV problems, intracranial tumors - complexity of the syndrome leads to a treatment of individual problems but not of the syndrome - dentist is usually first to diagnose syndrome due to the presence of multiple OKC |
|
Lateral Periodontal Cyst
|
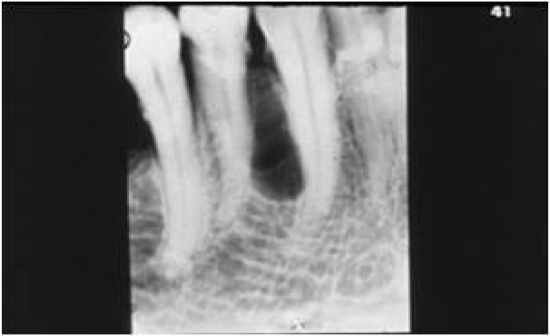 - a slow-growing, non-expansive developmental odontogenic cyst derived from one or more rests of the dental lamina containing an embryonic lining of 1-3 cuboidal cells and distinctive focal thickenings (plaques) - found between two adjacent teeth in the bone, common in the posterior mandible, rarely change shape and lined by NON-keratinized |
|
Butryoid Odontogenic Cyst
|
 - a type of lateral periodontal cyst that shows a multilocular growth pattern (looks grapelike) - these are many cystic cavities which are lined by the same epithelium as the lateral periodontal cysts |



