Cards In This Set
| Front | Back |
|
What are carbohydates - composition, definition, general formula.
|
*biomolecules composed of C,H, and O
*defined as plyhydroxyaldehydes or ketones
* Cx(H20)y - if x and y are 6, this is a hexose
|
|
What are the functional groups found in carbs?
|
-H-C=O (carbonyl, aldose)
-C=O- (keto, ketose)
*all contain -OH (hydroxyl) groups
|
|
What are the 2 ways to classify carbs? Give examples.
|
*number of carbon atoms in the base unit - pentoses (5C)-ribose and deoxyribose
*number of sugar units-mono (1), di (2), oligo(3-10), poly(>10) hexose units
|
|
What is stereochemistry? WHat are the 2 forms of sugars? What form do we use?
|
*study of the spatial arrangement of molecules
*D and L - we use D
|
|
What are the similarities and differences with stereoisomers (4)?
|
*same empirical structure
*different spatial arrangement
*different optical activity
*different biological properties
|
|
What is the other name for the D and L forms? What are their properties?
|
Enantiomers
*can't be superimposed
*mirror images
|
|
What is the chiral carbon? What is the importance of the chiral carbon to stereoisomers?
|
*C with 4 different groups attached to it
*must have at least 1 chiral center to have stereoisomers
|
|
How many enantiomers are possible per chiral carbon? How many biologically active isomers?
|
2^n, number of biologically active is half the number of enantiomers
|
|
Give the Fisher projections for L and D glucose
|
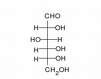 L is the mirror image |
|
What is the simplest sugar?
|
D-glyceraldehyde
|
|
Most important sugar in the diet
|
D-glucose
|
|
Sweetest of all sugars
|
D-fructose
|
|
D-galactose
|
Part of milk sugar
|
|
Used in RNA
|
D-ribose
|
|
What does a solution of an optical isomer do to light?
|
Rotates it in one direction
|



