Cards In This Set
| Front | Back |
|
Human Movement System
|
Combination and interrelation of the nervous, muscular, and skeletal systems.
|
|
Kinetic Chain
|
Combination of the nervous, skeletal, and muscular systems to produce human movement.
Chain of nerves, muscles, and joints. |
|
Nervous System
|
2 Parts:
Central Nervous System - Brain and Spinal Cord Peripheral nervous system - only nerves and connects brain and spinal cord with rest of body 3 primary functions Sensory function - ability to sense changes in internal or external environment Integrative function - ability to analyze and interpret sensory information to allow decision making Motor function - neuromuscular response to sensory info, such as causing a muscle to contract when stretched to far |
|
Neuron
|
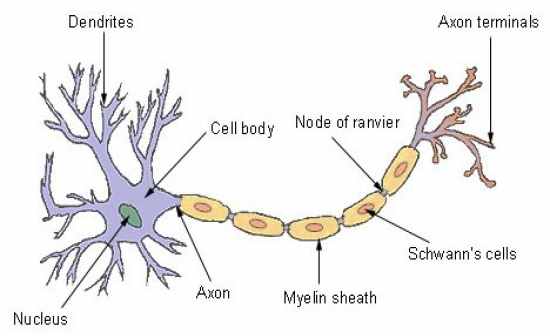 -Functional Unit of the nervous system. -Specialized cell that processes and transmits information through electrical and chemical signals. -3 Parts: Axon - provides communication from the brain and spinal cord to other parts of the body Cell Body - Contains a nucleus and other organelles, including lysosomes, mitochondria, and a Gogli complex. Dendrites - Gather information from other structures and transmit it back into the neuron. |
|
3 classifications of Neurons
|
Sensory - Transmit nerve impulses from effector sites (such as muscles and organs) via receptors to the brain and spinal cord.
Interneurons - Transmit nerve impulses from one neuron to another. Moter (Efferent) Neurons - Transmit nerve impulses from the brain and spinal cord to effector sites. |
|
Central Nervous System
|
 The portion of the nervous system consisting of the brain and spinal cord. Its primary function is to coordinate the activity of all parts of the body. |
|
Peripheral Nervous System
|
Consists of nerves that connect the CNS to the rest of the body and external environment.
-12 cranial nerves -31 pairs of spinal nerves which branch out from the brain and spinal cord -Sensory receptors. 2 Subdivisions: Somatic - consists of nerves that serve the outer areas of the body and skeletal muscle, and are largely responsible for the voluntary control of movement. Autonomic - divided into symapthetic and parasympathetic nervous systems. Both systems serve to increase levels of activation in preparaytion for activity (sympathetic) or to decreased levels of activation during rest and recovery (parasympathetic). |
|
Mechanoreceptor
|
-Sensory receptors responsible for sensing distortion in body tissue.
-Respond to outside forces such as touch, pressure, stretching, sound waves, and motion and transmit impulses through sensory nerves. -enable us to detect touch, sounds, and motion of the body and to monitor our proprioception. |
|
Muscle Spindles
|
 -Sensory receptors sensitive to changes in length of a muscle and the rate of change. -When a muscle is stretched, the spindles within also stretch which conveys info about its length to CNS via sensory neurons. -Help regulate contraction of muscles via stretch reflex mechanism. When a spindle stretches, an impulse is sent to spinal cord, and a response to contract the muscles is recived. -The rapid response is protective to prevent overstretching and potential muscle damage |
|
Golgi Tendon Organs
|
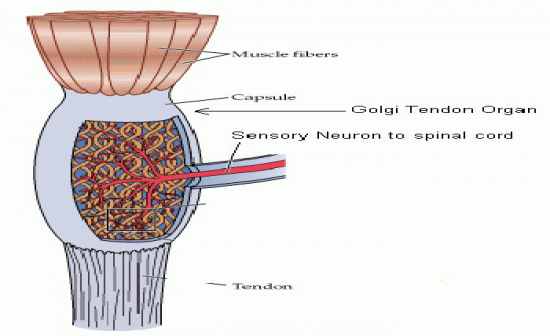 -Sensory Receptors sensitive to change in tension of the muscle and rate of that change -Located at the point where skeletal muscle fibers insert into the tendons of skeletal muscle. -Activation of the Golgi Tendon causes the muscle to relax, which prevents the muscle from excessive stress and possibility of injury. |
|
Joint Receptors
|
Receptors surrounding a joint that respond to pressure, acceleration and deceleration of the joint.
-Signal extreme joint positions to help prevent injury. -Also act to initiate a reflexive inhibitory response in the surrounding muscles if there is too much stress placed on that joint. |
|
4 types of sensory receptors are ____, ____, ____, & ____
|
-Mechanoreceptors
-Muscle Spindles -Gogli Tendon Organs -Joint Receptors |
|
Skeletal System
|
-Bodys framework, composed of bones and joints.
Important functions: -Provides shape and form for our body -Supporting -Protecting -Allowing bodily movement -Producing blood for the body -Storing minerals -Approximately 206 bones in the system, about 177 used in movement. All the bones form 300 joints. |
|
Bones
|
Provide a resting ground for muscles and protections of vital organs.
|
|
Joints
|
Junctions of bones, muscles, and connective tissue at which movement occurs. Also known as an articulation.
Connection of multiple bones with muscles and connective tissue |



