Cards In This Set
| Front | Back |
|
Name the five elements of plot
|
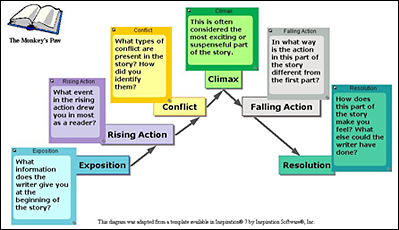 |
|
What type of character does not change through the course of the story?
|
STATIC character
|
|
What is the main character of a literary work called?
|
Protagonist
|
|
In a literary work, what is the character or force that is against the main character?
|
Antagonist
|
|
What type of character changes during the story, often as a result of what happens?
|
DYNAMIC character
|
|
What does "narra-" mean?Examples: narrator, narrative, narration
|
The telling of a story
|
|
What three things make up the setting of a story?
|
1. time2. place3. social backgroundIncludes:*geographic location
|
|
What are the five major types of conflict in a narrative work?
|
1. man vs. man2. man vs. self3. man vs. society4. man vs. nature5. man vs. technology
|
|
What is it called when we learn about a character by the writer making direct statements about the character's personality?
|
Direct Characterization
|
|
What is it called when we learn about a character through that character's thoughts, words, and actions; physical descriptions; and how other characters respond to that character, including what they think and say about him?
|
Indirect Characterization
|
|
What type of character is convincing, true-to-life, with many personality traits?
|
Round Character
|
|
What type of character is stereotyped, shallow, and often symbolic? They often only have one or two personality traits.
|
Flat Character
|
|
What is the structure of the story called, where the events and actions are arranged in a particular sequence?
|
PLOT
|
|
What is the dramatic struggle between two forces in a story called?
|
CONFLICT
|
|
What is the perspective from which the story is told called?
|
Point of View
|



