Cards In This Set
| Front | Back |
|
What is the CNS?
|
Made up of the Brain and Spinal Cord. Receives information from the whole body, examines it and then sends it out to the specific parts of the body telling them what to do.
|
|
What is the PNS?
|
Made up of sensory receptors and verves. Continuously informs the CNS of changes in conditions and then transmits the decisions back to effector ergans.
|
|
What does a neuron look like?
|
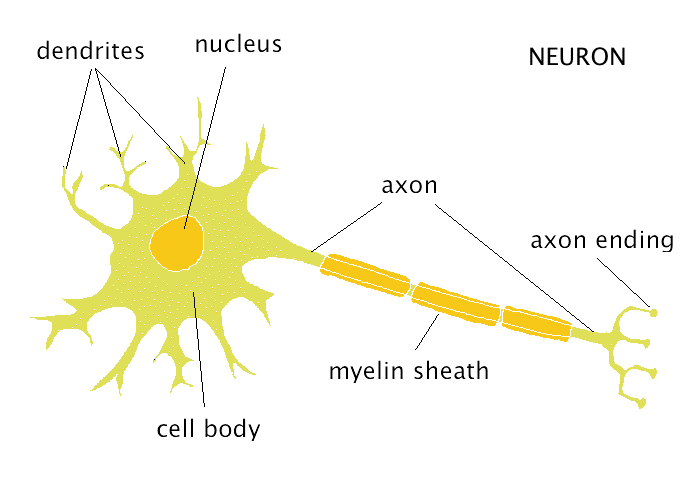 .. |
|
What do the Dendrites do?
|
Make contact with other cells and receive information from them.
|
|
What do does the Axon do?
|
Carries information away from the cell.
|
|
What does the Myelin Sheath do?
|
Encases the axon, insulating it and allowing messages to pass quickly along it.
|
|
What is the Nucleus?
|
The control centre of the cell. Carries Genetic information (DNA)
|
|
What is the Cell Body?
|
Central part of the cell, where all of the reactions take place.
|
|
What do Axon Terminals do?
|
Where the nerve ends, sends messages to muscle fibres.
|
|
What are Synapes?
|
The small gap between neurons. Messages cross this gap not as electrical impulses but as special chemicals called Neurotransmitters.
|
|
What are the advantages of Neurotransmitters?
|
The messages can be filtered so that a lot of the meaningless messages don't get though.
|
|
What are the disadvantages of Neurotransmitters?
|
Slow the messages down
|
|
What is white matter?
|
The inside part of the brain where all of the connections happen, white because of the myelin.
|
|
What is grey matter?
|
- The cerebrem. - Makes up 90% of the brain.- Responsible for complex thoughts.- Grey because of grey neurons.
|
|
What is cerebrospinal fluid?
|
The fluid in which the brain sits. It protects the brain.
|



