Cards In This Set
| Front | Back |
|
Mollusca-Class Bivalvia
|
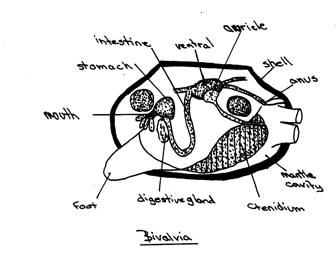 Includes hardshell clam (Mercenaria), Freshwater muscle (Anodonta) Oyster (Crassostrea) Oysters have specialized structures (catch muscles) and lack Anterior adductor muscle. |
|
Exterior Structure (bivalvia)
|
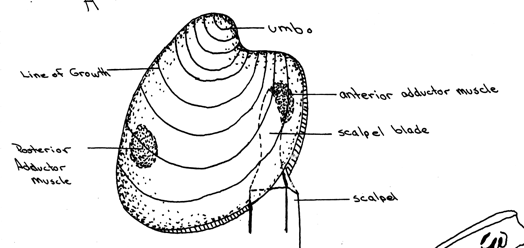 The bulge of the shell is the umbo |
|
Interior Structure (bivalvia)
|
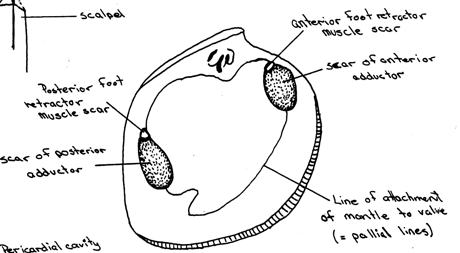 Left side has adductor muscle scars |
|
Internal Anatomy bivalvia
|
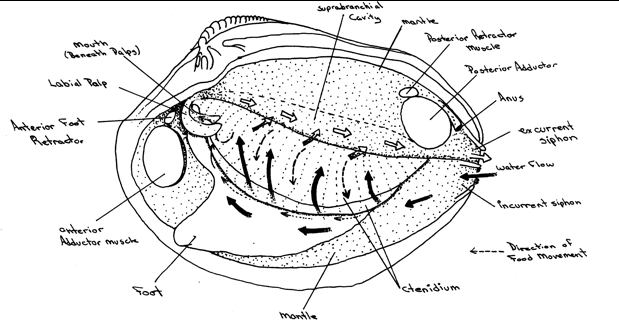 Internal anatomy of Mercenaria mercenaria, with the left valve and mantel removed. Arrows indicate water flow; dark arrows in the mantel cavity light arrows in the epibranchial cavity. *anterior and posterior adductor muscles *Pericardium (dorsal side) *Ctendidium responsible for the food caption and selection of material *Labial palps |
|
Internal anatomy bivalvia with mantel
|
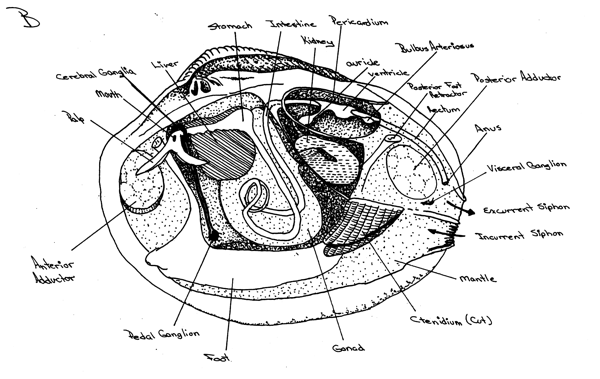 Internal anatomy with the left valve, mantel, ctenidia, and tissue overlying the internal organs all removed. *anterior and posterior adductor muscles *Pericardium (dorsal side) *Ctendidium responsible for the food caption and selection of material *Labial palps |
|
Differences between Mercenaria and Crassostrea
|
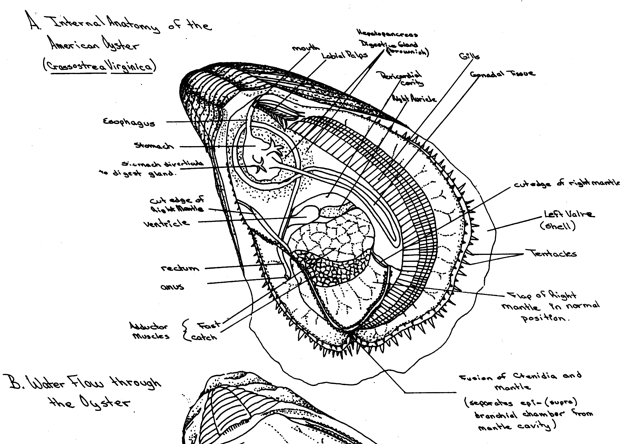 Oysters have specialized structures (catch muscles) and lack Anterior adductor muscle. Lack foot. the shell has been enlongated along the dorsal-ventral axis |
|
Class Polyplacophora (Amphineura)
|
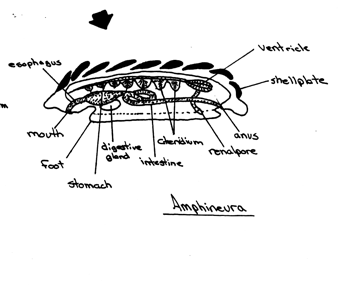 Worm like mollusc with a shell reduced to scattered spicules between the mantle edge and the foot is a groove (the pallial groove) in which the ctenidia lie Example; Chiton |
|
Class Gastropoda
|
Has a torsion of the body 180 degrees
anus (mantle cavity) and mouth occupy an anterior position
|
|
Subclasses Prosobranchs (class gastropoda)
|
Cowry (very fine calcium carbonate on the periostracum (outside) making it look glass when dead
Abalone (haliotis) (multiple holes for anus as it grows, thicker periostracum layer)
Note that the spiraling of the shell may look like a single spiral however it is just the out spiral that covers the inside ones.
|
|
Subclass Opistobranchs (class gastropoda)
|
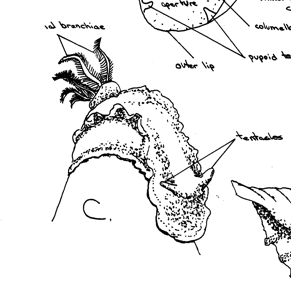 Reduced shell with detorsion with gills and mantle cavity either lateral or posterior. dorsal side has retractile pinnate and branchiae around the dorsal anus Example nudibranchs |
|
Subclass Pulmonates (class gastropoda)
|
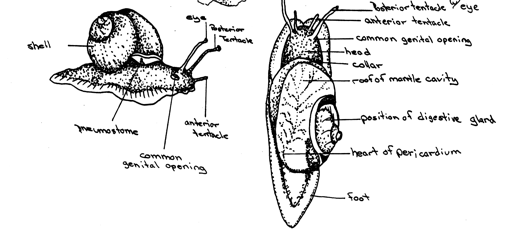 Pulmo; lung Latin. mostly land or freshwater snails with coiled shells and some torsion. Lung that opens to the outside (pnuemostome) |
|
Three layers of the shell
|
Periostracum-outside thin proteinaceous usually brown in color
Prismatic layer- middle composed of calcium carbonate and may be pigmented especially in the bivalves and gastropods.
Nacreous layer- inner most layer (mother of pearl) closest to the mantle surface.
|
|
Class bivalve locamotion
|
Two different foot muscles
1. foot muscle 2. foot retractor muscle
mantle muscle which controls the opening into the shell by pushing together along the open margin
The tentacles that may be extended and withdrawn along the edge of the mantle.
|
|
Class Bivalve development
|
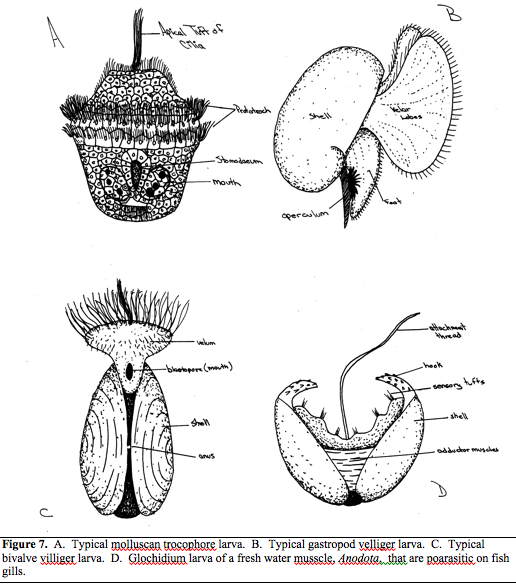 Two types of larvae 1. Trochophore tranforms into velliger larvae 2. Glochidium larvae |
|
Class Cephalopoda
|
Head-foot complex is dominant
no shell except in the nautilus (floating shell)
Soft fleshy mantle
|



