Cards In This Set
| Front | Back |
|
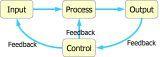
Model of generic process
|
 Pic |
|
Types of information systems
|
O There are many types of information systems
o Six common systems are found in most businesses
· Transaction processing systems (TPS)
· Management Information Systems (MIS)
· Executive Information Systems (EIS)
· Decision Support Systems (DSS)
· Communication Support Systems
· Office Support Systems
o Business systems center around transactions
o Systems must adapt to changing technology
|
|
The main responsibility as a system analyst
|
Develop system requirements and design models
Define problem and outline solution
|
|
The main challenge that a system analyst is facing
|
Develop alternatives consistent with corporate strategy
|
|
Required skills of the systems analyst
|
O Analysts manage issues ranging from technical to interpersonal
o Analysts must commit to lifelong learning
o Technical Skills and Knowledge
o Business Skills and Knowledge
o People Skills and Knowledge
|
|
Technical Skills and Knowledge
|
· Should grasp many types of technologies
· Be informed of tools and techniques
· Common Software Tools:
v IDEs
v CASE
· Common Techniques:
v Project Planning
v Cost Planning Analysis
v Architectural Analysis
|
|
Business Skills and Knowledge
|
· Understand organizational structure
· Understand business concern
· Study business administration
|
|
People Skills and Knowledge
|
· Knowledge of people center around thinking and feeling
· Used to adapt systems to users
· Ability to listen empathetically
|
|
UML History
|
· OO concepts became very popular in early 90s, resulting in many different technologies and notations
· In 1995, Rational Software created a standard set of techniques/methodologies to OOSAD known as Unified Modeling Language (UML)
· Rational was sold for $2.1B to IBM on February 20, 2003
|
|
UML Definition
|
A language for modeling object-oriented software, used for visualizing, specifying, constructing, and documenting
|
|
UML Building Blocks
|
· UML model is composed of three building blocks:
v Things- modeling elements, such as classes, use cases, activities, etc.
v Relationships- these tie things together and specify how two or more things are semantically related, such as association, aggregation, generalization, etc.
v Diagrams- view into UML models
§ They contain collections of things and relationships used to visualize what the system will do and how it will do it
|
|
Difference between SAD and OOSAD
|
O SSAD
· Starts from identifying processes
o OOSAD
· Starts from identifying objects and their relationships
|
|
The strengths of object technology
|
O Reflects a single paradigm
o Facilitates architectural and code reuse
o Reflects real world models more closely
o Encourages stability
o Is adaptive to change
|
|
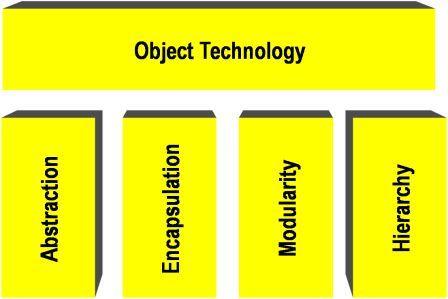
Basic principles of object technology
|
 Pic |
|
Major Enterprise-Wide Systems (ERP vs. CRM vs. SCM)
|
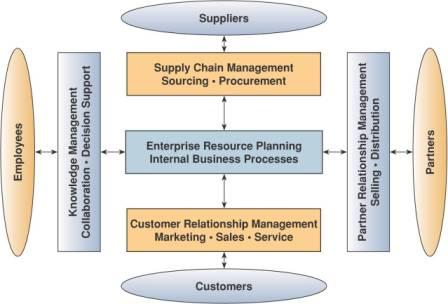 · CRM and SCM: o Main focus is on external processes of a business o Includes internal processes that interact with either customers (CRM) or suppliers (SCM) · ERP: o Main focus is on internal processes of a business, cross-functional |



