Cards In This Set
| Front | Back |
|
M-phase chromatin is...?
|
Tightly packed into visible chromosomes
|
|
Most eukaryotic DNA is packaged into..
|
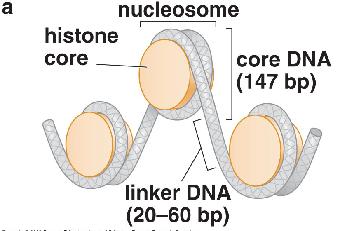 Nucleosomes |
|
DNA between nucleosomes is...
|
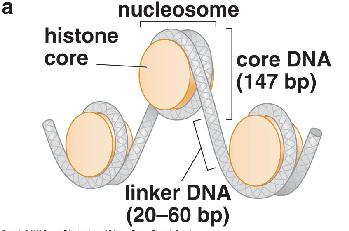 Linker DNA |
|
DNA most tightly associated with the nucleosome is called..
|
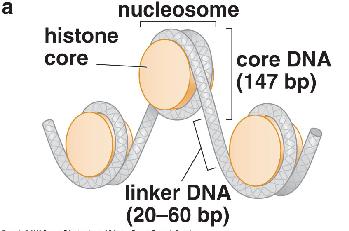 Core DNA (wrapper around histone core) |
|
The histone core comprises these four histone proteins
|
H2A . H2B . H3 . and H4
|
|
Histone core is _____ charged
|
Positively (this is why DNA -neg charged- associates with it
|
|
all human
histones contain no less than 20% of these particular amino acids.
|
Lysine and arginine (both pos charged)
|
|
Histone fold domain
|
which is
“conserved” (the same) for all the core
histones, can assemble intermediate structures
without DNA. (H2A/H2B diamer and H3/H4 tetramer
|
|
Histone helices
|
The cylinders represent protein “helices” (called
α-helices) that look a lot like a DNA helix!
|
|
Histone H1
|
Binds to linker DNA btw nucleosomes
|
|
Histone h1 binds to 2 regions
|
1) The linker DNA on one side of the nucleosome;
2) The center of the 147 bp “protected” DNA,
at the “dyad axis” (basically, the “center”).
|
|
Size of fiber w/o H1
|
W/o= 30nm
w=10nm
(closely together)
|
|
Solenoid model
|
 nucleosome discs are stacked on “edge” in the form of a helix, and the linker DNA is buried in thecenter of the “superhelix” but it never passes through or crosses the axis of the 30 nM fiber itself. |
|
Zig-Zag model
|
 the 30 nM fiber is a compacted form of “zigzag” nucleosome arrays, and the linker DNA must pass straight through the central axis of the fiber |
|
"N" terminal tails
|
Of core histones are CRUCIAL in forming 30nm fibers
|



