Cards In This Set
| Front | Back |
|
Functions of Blood
|
1. Transports gases and nutrients
2.Regulation of PH and osmosis 3.Maintenance of Body temperature. 4.Protection against foreign substances 5.Clot Formation |
|
Composition of Blood
|
55% Plasma - 91 % water 7 % proteins
45 % formed elements |
|
Plasma
|
Liquid Part of Blood
Ions Nutrients Waste Products Gases Regulates Substances - hormones, enzymes |
|
Proteins of Plasma
|
Albumins - Viscosity, Osmotic Pressure, Buffer, Transports Fatty Acids, Free bilirubin, thyroid hormones
Globulins - Transports Lipids, Carbohydrates, Hormones, Ions, Antibodies Fibrinogen - Blood Clotting |
|
Red Blood Cells (erythrocytes)
|
Contains Hemoglobin, Transports oxygen and carbon dioxide
1/3 Hemoglobin 2/3 Lipids RBCs last 120 days in circulation |
|
White Blood Cells (leukocytes)
|
Protects body against microogranisms and remove dead cells and debris
Granulocytes - Cytoplasm contains large granules, have multi lobed nuclei. Has 3 distinctive types : Neutrophils, eosinophils, basophils O |
|
Platelets (thrombocytes)
|
Form Platelet plugs, release chemicals necessary for blood clotting
|
|
Hematopoiesis
|
Process of Blood Cell Production
|
|
Carbon Dioxide from tissues to lungs
|
7 % dissolved in plasma
23 % in combination with hemoglobin 70 % transported as bicarbonate ions produced as a result of combination of H20 and Co2 because of enzyme carbonic anhydrase found within RBCs |
|
Erythropoietin
|
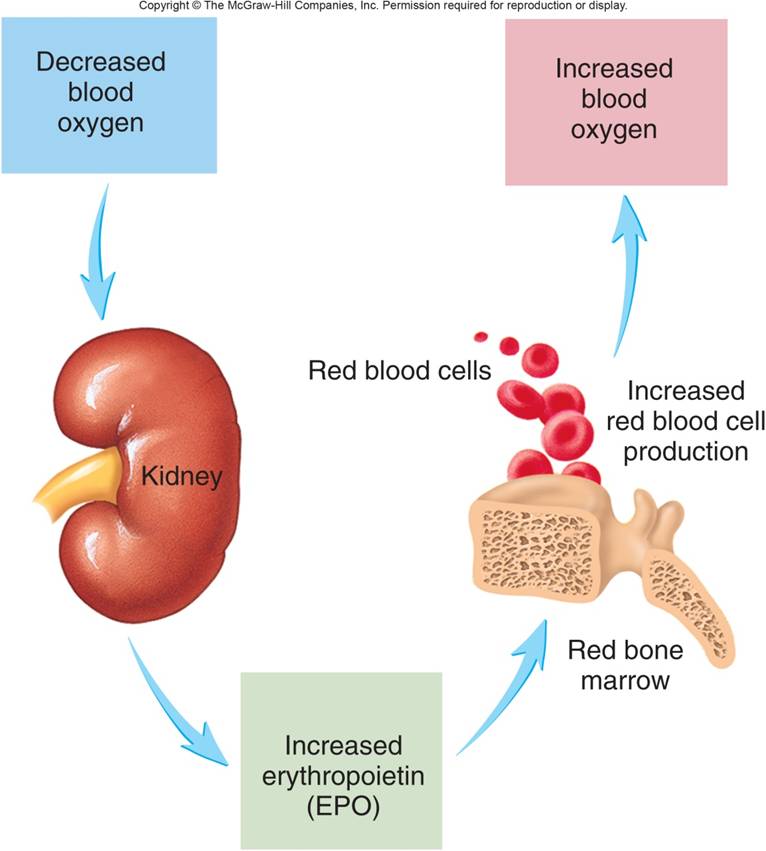 A hormone that stimulates RBC production. Produced by kindeys in response to low blood 02 levels |
|
Hemoglobin Breakdown
|
Broken down by macrophages into heme and globen chains
Globen chains of hemoglobin are broken down to amino acids and are metabolized or used to build new proteins |
|
White Blood Cells other questions
|
Ameboid - pseudopodia make them move like amoeba
Diapedesis - cells become thin, elongate and move either between or through endothelial cells of capillaries Chemotaxis - attraction to and movement toward foreign materials or damaged cells |
|
Neutrophils
|
Secrete Lysozome
Accounts for 60-70 % of WBC |
|
Eosinophils
|
Enter tissues during inflammatory response.
prevelant in allergic reactions and parasitic infections 2-4 % of WBC |
|
Basophils
|
Inflammatory and allergic reactions
Produce histamine and heparin Less than 1 % of the WBC population |



