Cards In This Set
| Front | Back |
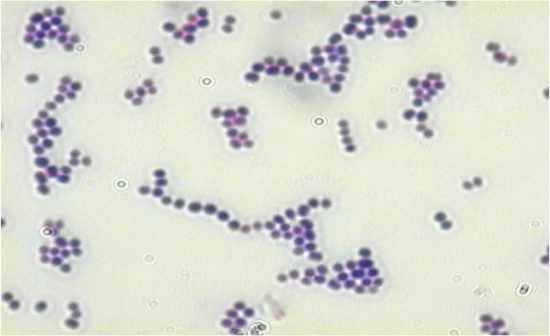 |
Gram stain: Gram positive cocci
Staphylococcus aureus Crystal violet, iodine, acetone/alcohol, safranin Usually susceptible to antibiotics and disinfectants Skin infections, MRSA, food poisoning |
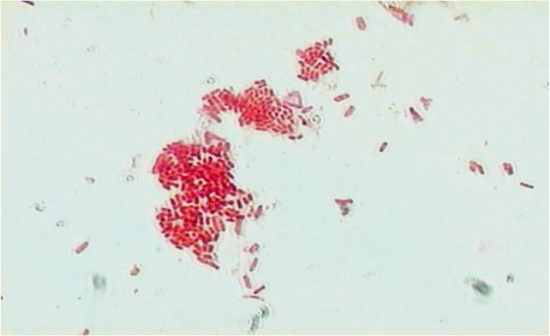 |
Gram stain: Gram negative bacilli
Escherichia coli Crystal violet, iodine, acetone/alcohol, safranin Relatively resistant to antibiotics and disinfectants Normal flora, sometimes UTI, food poisoning |
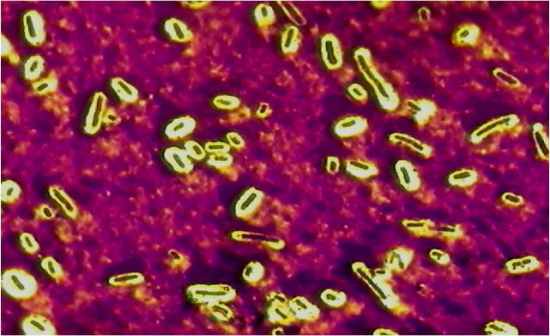 |
Capsule stain
Klebsiella pneumoniae Crystal violet, copper sulfate rinse Skim milk broth, lactose sugars, antiphagocytic Pneumonia, meningitis |
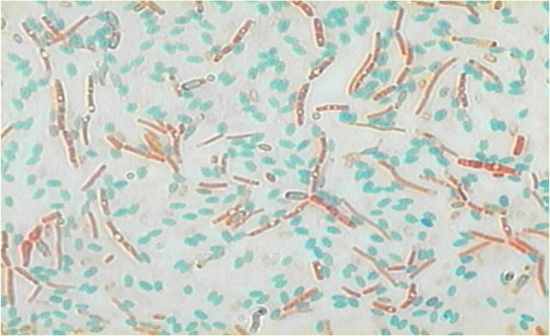 |
Endospore stain
Bacillus cereus Boiling water bath, malachite green, safranin (RT) Protected structure with dipocolinic acid core, peptidoglycan cortex, protein coat Anthrax, tetanus, botulism, gangrene |
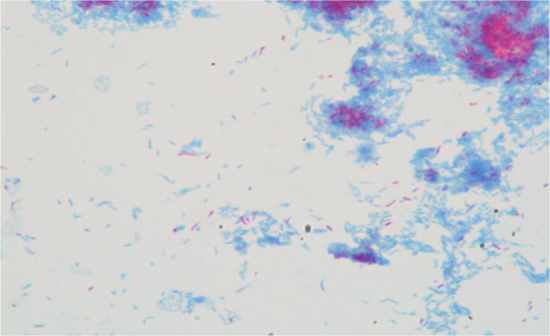 |
Acid Fast stain
Mycobacterium smegmatis Boiling water bath, carbol fuschin, acid/alcohol rinse, methylene blue (RT) Mycolic acid protects from drying, disinfection TB and Leprosy |
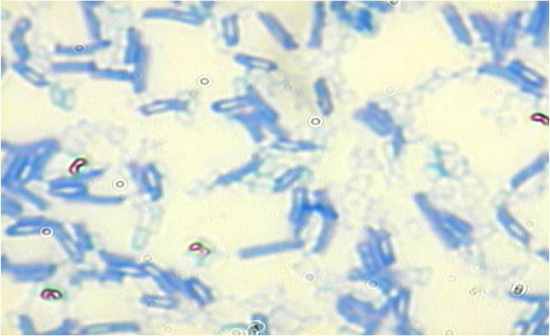 |
Inclusion Bodies stain
Bacillus subtilis Dextrose agar, methylene blue simple storage of carbohydrates and fatty acids Produces spores also Anthrax, tetanus, botulism, gangrene |
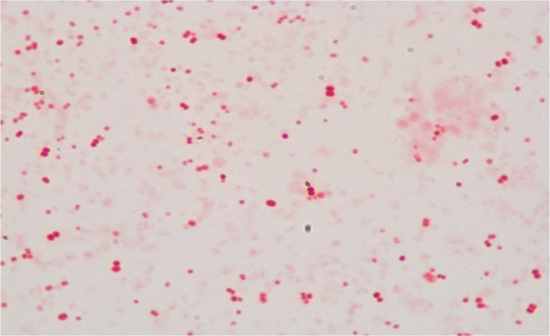 |
Gram Stain: Gram negative cocci in pairs
Neisseria sicca Crystal violet, iodine, acetone/alcohol, safranin Oxidase postive Meningitis and gonorrhea |
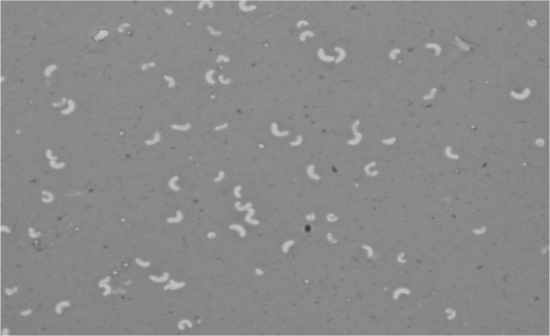 |
Negative stain: spirals (vibrios and spirilla)
Rhodospirillum rubrum nigrosin with blood smear technique only spiral used in class (Gram -), only acidic dye other negative technique: capsule Cholera and Campylobacter |
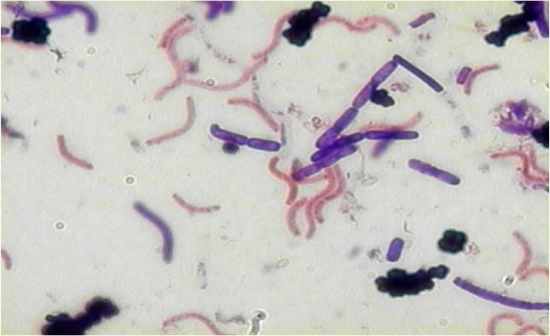 |
Mixed Gram stain: - spirals, + rods,+ cocci in tetrads
Rhodospirillum, Bacillus, Micrococcus mixtures common in clinical specimens Gram + variability due to amount of peptidoglycan |
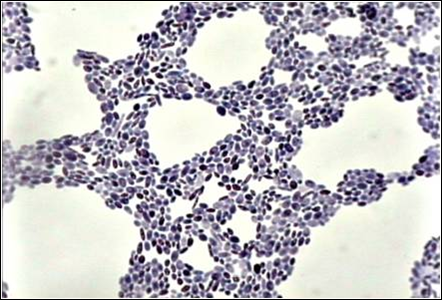 |
Gram Stain: yeast
Saccharomyces cereviseae Bakers, Brewers yeast Alcoholic fermentation with gas production Candida causes vaginitis and thrush |



