Cards In This Set
| Front | Back |
 Label |
1. Oblugate aerobe
2. facultative anaerobe 3. aerotolerant 4. obligate anaerobe |
|
Carbohydrate Fermentaion & Gas Production Test
1. How do you perform test? 2. Why? 3. media and reagents used? 4. results |
1. by inoculating broth via loop
2. tests for bacteria's ability to ferment sucrose/lactose/mannitol and produce gas and/or an acid end-product 3. broth contains beef extract, the specific sugar, and a phenol red indicator to indicate acid end product, a durham tube is added to indicate gas production. 4. + for acid is yellow (indicating fermentation) + for gas is gas bubble in durham tube - gas is no bubble - for acid is no color change or reddish orange color |
 Carbohydrate Fermentaion & Gas Production Test Results |
1 - negative acid / negative gas
2A - must incubate longer 2B - positive acid / neg. gas 3A - positive acid / positive gas |
|
Mixed Acid Fermentation Test
1.How do you perform test? 2. Why? 3. media and reagents used? 4. results |
1. Inoculate broth with loop
2. tests for bacteria's ability to use the mixed acid pathway, which produces acidic end products such as lactic, acetic, and formic acid when glucose is fermented 3. broth contains peptone, glucose and phosphate buffer. A methyl red indicator is added to indicate acid end products 4. Red - positive orange - yellow - negative |
 Mixed Acid Fermentation (MR) Test Results |
1st is control
2nd neg. 3rd is positive |
|
Citrate Test
1. How do you perform this test? 2. Why? 3. Results |
1. Inoculate slant with needle and stab
2. bacteria that has the ability to consume citrate as the sole source of carbon, and ammonia salt as the sole source of nitrogen 3. + is blue (meaning bacteria metabolized citrate and pH increased. - remains green |
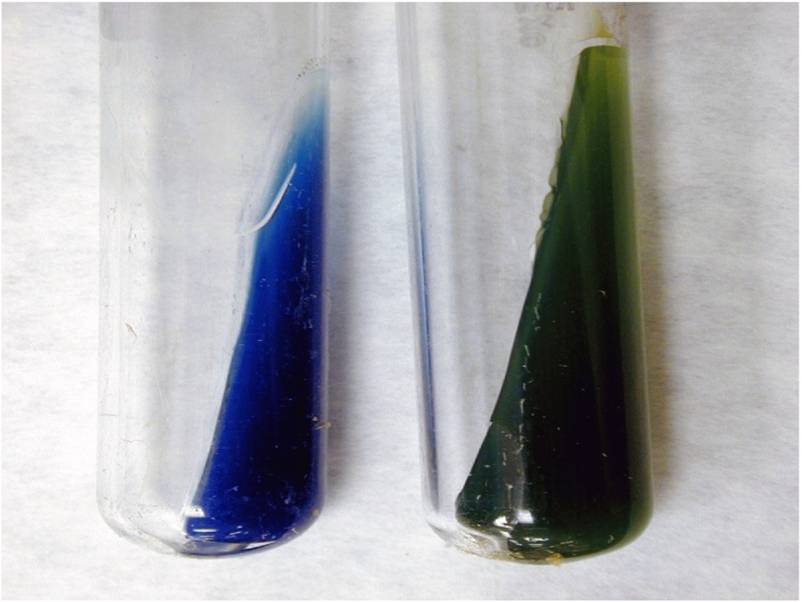 Citrate Test Results |
Blue is +
Green is - |
|
Urea Hydrolysis Test
1. How do you perform this test? 2. Why? 3. Media & Reagents used. 4. Results |
1. inoculate urea broth with loop
2. determine bacteria's ability to hydrolyze urea to make ammonia using the enzyme urease 3. Urea broth and phenol red indicator 4. urea broth is naturally yellow gold color, if the enzyme urease hydrolyzes urea to make ammonia it will turn a bright pink color - if no change in color or color is orange(ish) |
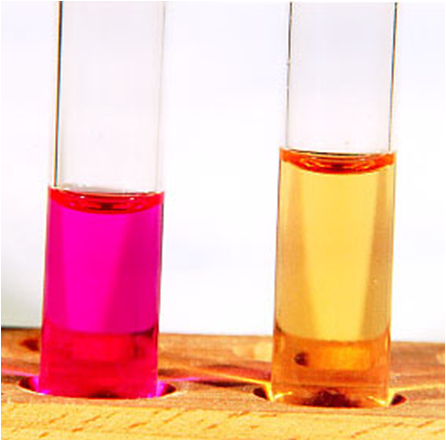 Urea Hydrolysis Results |
1st is positive
2nd is negative |
|
Tryptophan Degradation Test
1. How to perform 2. Why? 3. Media and reagents used 4. Results |
1. Inoculate tryptone broth with loop
2. tests for bacteria's ability to produce indole, the enzyme tryptophanase breaks down tryptophan, indole is of the byproducts 3. tryptone broth contains tryptophan, a kovac reagent is used 4. after kovac's reagent is used, it + kovacs will react with indole and make a red colored line on top, negative there is no red line |
 Tryptophan Degradation Test Results |
See question
|
|
Catalase Test
1. How to perform test 2. why? 3. results |
1. streak plate. after incubation add H2O2 to the colonies, observe for bubbling
2. testing for the bacteria's ability to produce catalase that breaks down H2O2 onto water and CO2 3. Bubbles formed = + no bubbles = - |
|
Starch Hydrolysis Test
1. How to perform 2. why 3. media and reagent used 4. results |
1. divide starch plate in 2 with marker on bottom of plate, streak control on one side, bacteria specimen on other
2. Testing for exoenzymes, inculding a-amylase and oligo -1, and 6 - glucosidase that hydrolyze starch. Starch is too large to enter bacter cell, so the bacteria may sevret exoenzymes to degrade the starch into subunits that can be used by the organism 3. starch agar is a simple nutritive agar with starch added. Iodine is added, since no color change occrurs in medium when organisms hydrolyze the starch. 4. A clearing around the bacterial growth indicates the organism, has hydrolyzed the starch. |
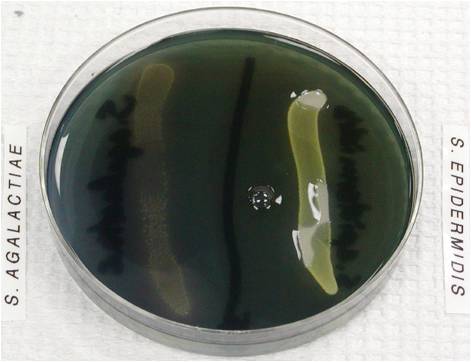 Strach Hydrolysis test results |
Left is -
Right side is + |
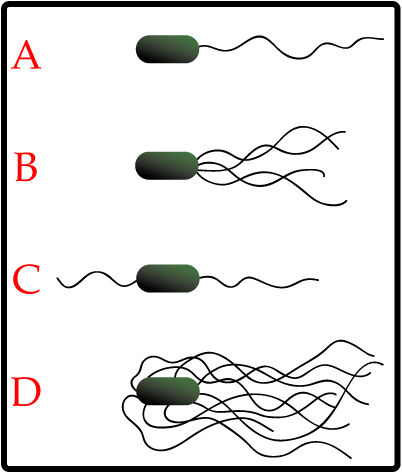 Label |
A - Polar
B - lophotrichous C - peritrichous D - amphitrichous |



