Cards In This Set
| Front | Back |
|
Pneumonia + Hepatitis
|
Q Fever
|
|
Sulphur Granules
|
Actinomyces israelii
|
|
Chlamydia pneumoniae
|
Atypical pneumonia. Upper and Lower respiratory infection.
|
|
Trachoma
|
Clamydia trachomatis - conjunctivities. Primarily in Africa. Immunotype A, B, C.
|
|
Reiter's Syndrome
|
Autoimmune. Antibodies against C. trachomatis attack urethra, joints, uveal tract.
|
|
Rickettsia prowazekii
|
Endemic typhoid. Flu-like --> maculopapular rash --> miningoencephalitis. Death from peripheral vascular collapse or bacteria pneumonia. Lice!
|
|
Rickettsia tutsugamushi
|
Scrub typhus. Vasculitis at site of lesion, rash, edema, hemorrhage, bacteremia. Mites or chiggers.
|
|
Ehrlicosis
|
Fever, headache, myalgia, thrombocytopenia, leukopenia, liver dysfunction. E. chaffensis (Lone Star tick, monocytes).
|
 What does the attached picture indicate? |
Leptospirosis
|
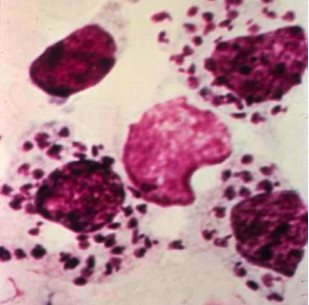 What does the attached picture indicate? |
Leishmaniasis
|
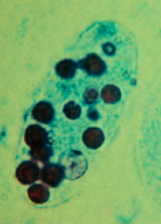 What does the attached picture indicate? |
 Entamoeba hystolytica, ingests RBCs. Picture here is of cyst with 4 nuclei. |
|
Life cycle of Entamoeba hystolytica
|
No animal reservoir. Cyst is ingested, trophozoite burrows into colon, ascending intestine.
|
|
What is Metronidazole used to treat?
|
Entamoeba hystolytica, Giardia lamblia
|
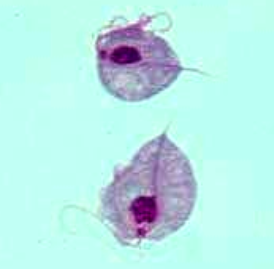 Jerky motion of trophozoites on wet-mount. |
Trichomonas vaginalis
|
|
Life cycle of Toxoplama gondi
|
Humans and other mammals are intermediate hosts. Cysts ingested in undercooked meat or cat feces. Cysts rupture in small intestine, invade intestinal wall, enter macs and differentiate into trophozoites. Bradyzoites are slow-growing cysts that persist in muscle, CNS, other tissues.
|



