Cards In This Set
| Front | Back |
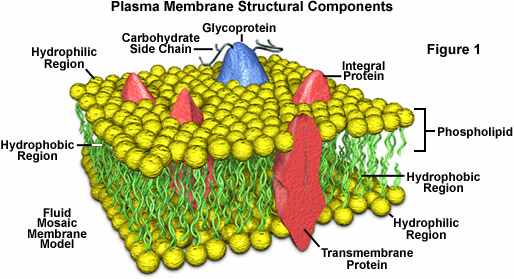 Plamsa Membrane |
A microscopic membrane of lipids and proteins that forms the external boundary of the cytoplasm of a cell or encloses a vacuole, and that regulates the passage of molecules in and out of the cytoplasm.
|
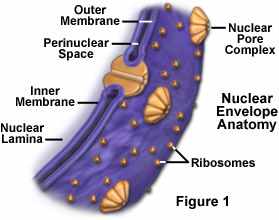 Nuclear Envelope |
A double-membrane structure that constitutes the outermost portion of the nucleus.
|
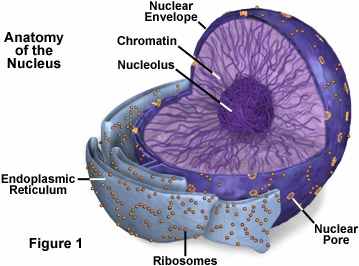 Nucleus |
A membrane bound structure that contains the cell's hereditary information and controls the cell's growth and reproduction.
|
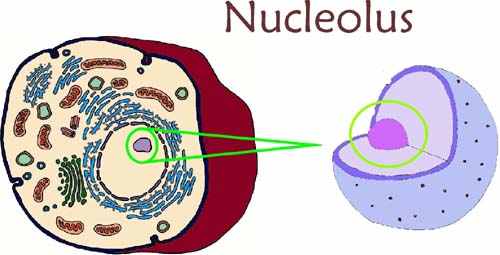 Nucleolus |
A small, typically spherical granular body located in the nucleus of a eukaryotic cell, composed largely of protein and RNA.
|
 Cytoplasm |
The material or protoplasm within a living cell, excluding the nucleus.
|
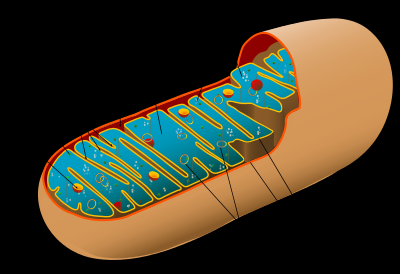 Mitochondrion |
An organelle found in large numbers in most cells, in which the biochemical processes of respiration and energy production occur. It has a double membrane, the inner layer being folded inward to form layers (cristae).
|
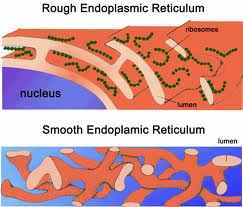 Endoplamsic Recticulum |
a network of membranous tubules within the cytoplasm of a eukaryotic cell, continuous with the nuclear membrane.
|
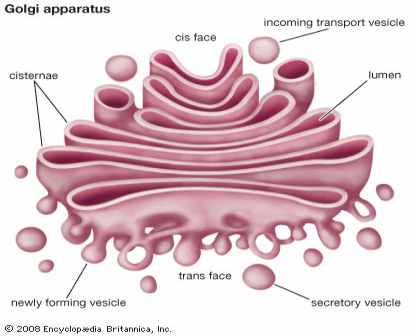 Golgi Apparatus |
A complex of vesicles and folded membranes within the cytoplasm of most eukaryotic cells, involved in secretion and intracellular transport.
|
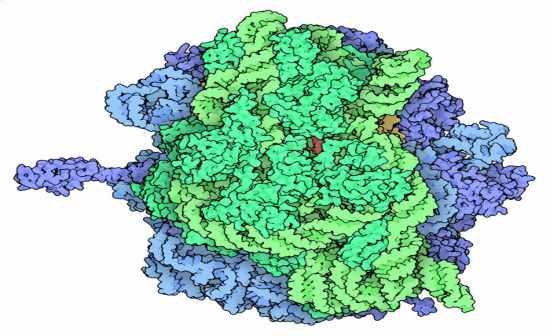 Ribosome |
An organelle consisting of RNA and associated proteins, found in large numbers in the cytoplasm of living cells. They bind messenger RNA and transfer RNA to synthesize polypeptides and proteins.
|
 Vacuole |
A space or vesicle within the cytoplasm of a cell, enclosed by a membrane and typically containing fluid.
|
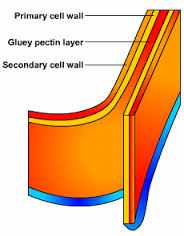 Cell Wall |
A rigid layer of polysaccharides lying outside the plasma membrane of the cells of plants, fungi, and bacteria.
|
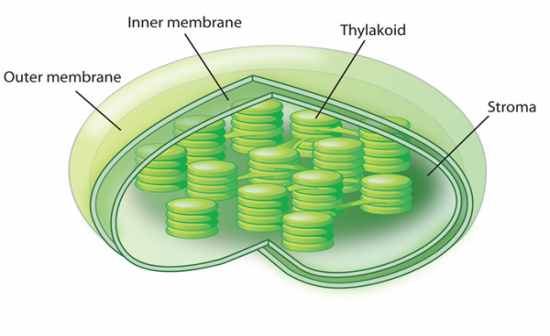 Chloroplast |
An organelle that contains chlorophyll and in which photosynthesis takes place.
|
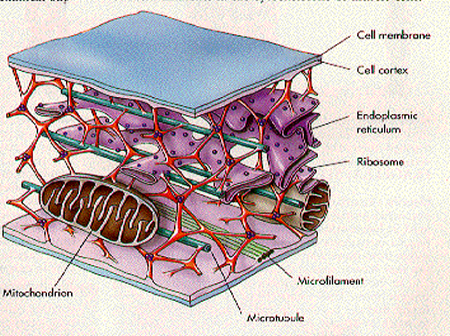 Cystoskeleton |
A microscopic network of protein filaments and tubules in the cytoplasm of many living cells, giving them shape and coherence.
|
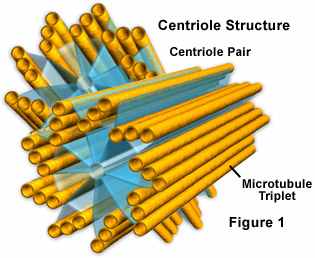 Centriole |
A cylindrical organelle near the nucleus in animal cells, occurring in pairs and involved in the development of spindle fibers in cell division.
|
 Cilium |
A short, microscopic, hairlike vibrating structure. They occur in large numbers on the surface of certain cells, either causing currents in the surrounding fluid, or, in some protozoans and other small organisms, providing propulsion.
|



