Cards In This Set
| Front | Back |
|
Vector
|
Vectors have magnitude & direction. Include displacement, velocity, acceleration, force, etc.
|
|
Scalar
|
Scalars are quantities w/out direction, only magnitude.
|
|
Dot Product
|
Multiplying 2 vectors using the dot product results in scalar quantity. Gotten by multiplying the vector's magnitudes & the cosine of the angle between them. (Ex: to find scalar quantity of work, we multiply the vector quantities of force & displacement) & then multiply by cosθ)
|
|
Cross Product
|
Multiplying 2 vectors by the cross product results in a vector quantity. Product of the vector's magnitudes & the sine of the angle between them. (Ex: find torque which is vector by multiplying force and lever arm which are also vectors, then multiplying by sinθ). Then use right hand rule to determine resultant vector's direction. Thumb goes in direction of vector A, fingers go in direction of vector B, & palm is the direction of the resultant C.
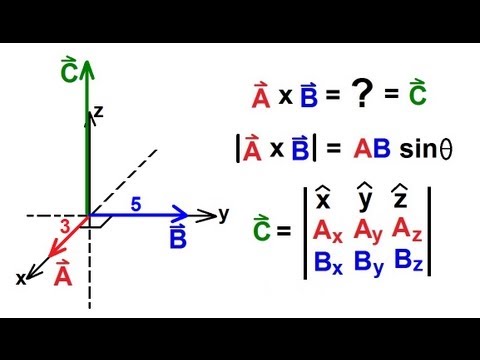 |
|
Displacement
|
Vector representation of position change. Path independent, equivalent to straight line distance between start & end locations.
|
|
Distance
|
Scalar quantity that reflects path traveled
|
|
Average Velocity (m/s)
|
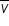 = =  x/ x/ t t 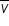 = average velocity (m/s) = average velocity (m/s) x = change in displacementt = time x = change in displacementt = time |
|
Average Speed (m/s)
|
V = d / t
|
|
Instantaneous Velocity
|
v = lim
 t - 0 t - 0  x/ x/ tThe limit of the change in displacement over time as the change in time approaches zero tThe limit of the change in displacement over time as the change in time approaches zero |
|
Instantaneous Speed
|
The magnitude of the instantaneous velocity vector
|
|
Force (Newtons, N, kg
 m/s2) m/s2) |
Any push or pull that can result in acceleration
|
|
Gravity
|
The attractive force between 2 objects as a result of their masses
|
|
Friction
|
Force that opposes motion due to electrostatic interactions between 2 object's surfaces
|
|
Static Friction
|
Exists between 2 objects that are not in motion relative to each other; can take on many values depending on the magnitude of the applied force
|
|
Kinetic Friction
|
Exists between sliding object & object on which it slides. Exists between 2 objects that are in motion relative to each other; constant value, unlike static friction which can have many values
|



