Cards In This Set
| Front | Back |
|
What is an atom?
|
An atom is composed of a Nucleus surrounded by at least one Electron
|
|
What is a nucleus?
|
A nucleus is composed of Neutrons (Neutral and heavier) and Protons (positively charged and slightly lighter)
Associated terms Nucleon, Strong Nuclear Force, Quark |
|
What is an electron?
|
An electron is a very small particle (negatively charged) which orbits the nucleons.
Note: The space between the nucleons, or nucleus, and the electrons create the bulk of the atom. |
|
What is an element?
|
All atoms are elements and thus can not be broken down further by chemical means. Elements are the building blocks of all compounds.
|
|
Element labels
|
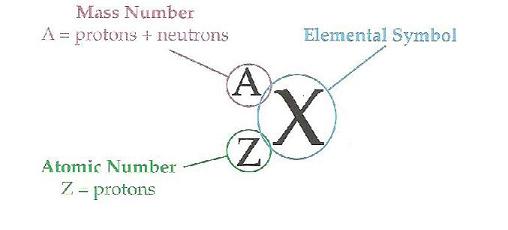  |
|
Element Identity
|
The Letter symbol and the number of Protons are always the identifyers of elements every other label can vary.
|
|
Isotopes
|
Isotopes are atoms of the same element which have a different number of nuetrons and thus a different mass.
Note: the number of protons always remains the same. |
|
What is atomic weight?
|
Atomic weight is weighted average of the masses of the isotopes for an element. Mass is listed in amu or u
|
|
How do you calculate Moles?
|
 Formula to Calculate moles: |
|
Avogadros number
|
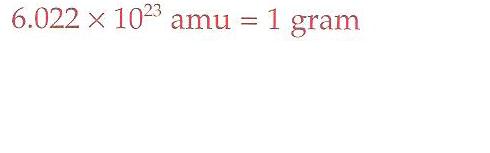 Is the number of amu in one gram |
|
Periodic Table Layout
|
Periods: horizontal rows
Groups: Columns Families of elements are as follows: 1. Metals: Alkali, Alkaline Earth, Transitional 2. Metaliods: thin diagonally flowing group 3. Non-metals: Covalent and pi bonding, Halogens, Nobel Gases |
|
General Characteristics of Metals
|
1. Take on positive charge in bonds
2. Form ionic bonds with oxygen (accept BeO) 3. Ductile 4. Malleable 5.Conduct heat and electricity 6. Lustrous |
|
Differences between types of metals
|
Alkali Alkaline
Lower melting point Higher melting point Highly reactive Less reactive Softer and less dense Harder and more dense +1 cation +2 cation |
|
Characteristics of Metaliods
|
Non descript some characteristics of metals and some characteristics of non metals
|
|
Important characteristics of non metals
|
1. Pi bond forming C, N, P, S, O
2. Halogens typically take on -1 charge however all but flourine can take on positive charges when paired with a highly electronegative atom |



