Cards In This Set
| Front | Back |
|
3 Main Types of Muscle
|
|
|
Skeletal Muscle
|
|
|
Smooth Muscle
|
|
|
Cardiac Muscle
|
|
|
Red Fibers (Slow-Twitch Fibers)
|
|
|
White Fibers (Fast-Twitch Fibers)
|
|
|
Intercalated Discs (& Gap Junctions)
|
Cardiac muscle cells are connected by intercalated discs which contain many gap junctions. Gap junctions are connections between the cytoplasm of adjacent cells, allowing for the flow of ions directly between cells. Allows for rapid & coordinated muscle cell depolarization & efficient contraction of cardiac muscle
|
|
Sarcomere
|
Basic contractile unit of striated (skeletal) muscle.
|
|
Troponin & Tropomyosin
|
Found on the thin filament & regulate actin-myosin interactions
|
|
Lines, Zones, & Bands of the Sacromere
|

 |
|
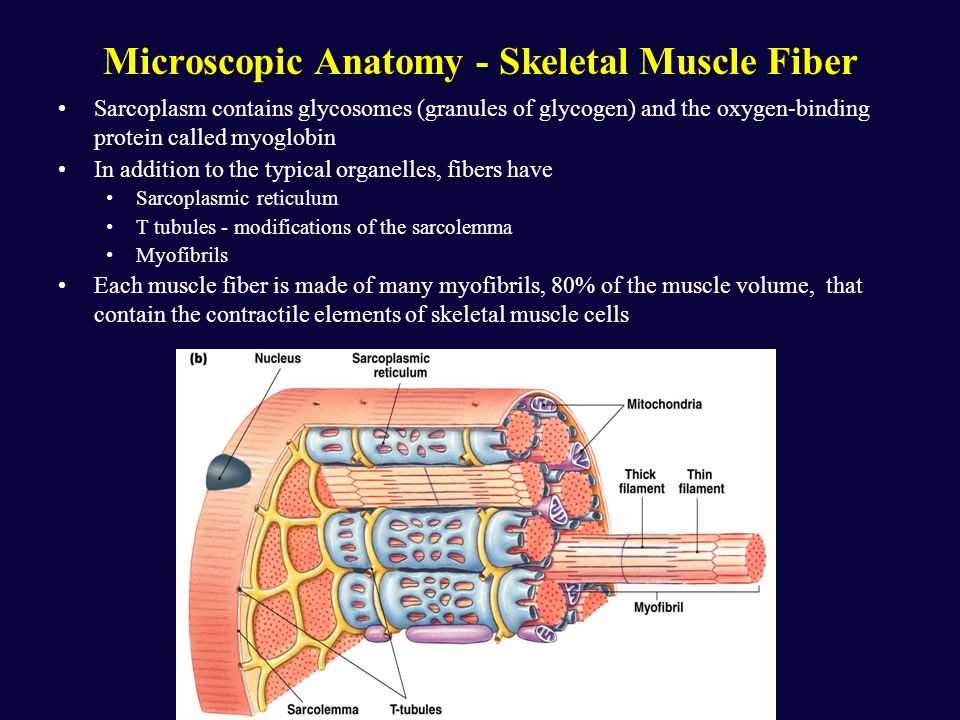
Myofibrils
|
Sarcomeres attach end to end to become myofibrils
|
|
Myocytes
|
A muscle cells or muscle fiber. Made up of many myofibrils
|
|
Sarcoplasmic Reticulum
|
Surrounds myofibrils, is a calcium-containing modified endoplasmic reticulum
|
|
Sarcolemma
|
Cell membrane of a myocyte
|
|
T-Tubules
|
A system of T-tubules is connected to the sarcolemma & oriented perpendicularly to the myofibrils, allowing incoming signals from nerves to reach all parts of the muscle
 |



