Cards In This Set
| Front | Back |
|
Deoxyribonucleic Acid (DNA) have the pentose called ___, where the 2' OH group is replaced by an ___. Ribonucleic Acid (RNA) have the pentose called ___, where both the 2' & 3' groups are OH.
|
|
|
Nucleoside vs. Nucleotide
|
Nucleosides are a 5-carbon sugar pentose, covalently bonded to a nitrogenous base at the C-1' of the sugar
|
|
Purines
|
PURe As Gold (as A & G are purines) gold wedding rings, need to rings to make a marriage. Adenine & Guanine are purines, & purines have 2 rings in their structure.
|
|
Pyrimidines
|
CUT the Pye (as C, U, & T are pyrimidines), pie has one ring of crust. Cytosine, Uracil, & Thymine are pyrimidines, which have one ring.
|
|
Requirements for Being Aromatic (4)
|
|
|
Watson-Crick Model of DNA Structure
|
|
|
Chargaff's Rule
|
Because of specific base-pairing, the amount of A always equals the amount of T, & the amount of C always equals the amount of G. Ex: If a sample of DNA has 10% G, what is the % of T?10% G = 10% C, thus G + C = 20%100% - 20% = 80% (A + T), therefore T = 40%
|
|
Histones
|
DNA that makes up chromosomes is wound around a group of small basic proteins called histones, which forms chromatin (the material of which chromosomes are made of).
 There are 5 histone proteins in eukaryotic cells w/ 2 copies each of H2A, H2B, H3, & H4 that form a core for about 200 base pairs of DNA to wrap around, forming a nucleosome. H1 seals off the DNA as it enters & leaves the nucleosome, stabilizing the structure. Nucleosomes make DNA more organized & compact. There are 5 histone proteins in eukaryotic cells w/ 2 copies each of H2A, H2B, H3, & H4 that form a core for about 200 base pairs of DNA to wrap around, forming a nucleosome. H1 seals off the DNA as it enters & leaves the nucleosome, stabilizing the structure. Nucleosomes make DNA more organized & compact. 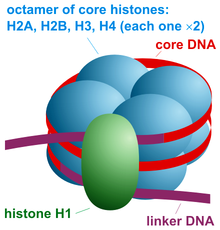 |
|
Nucleoproteins
|
Proteins that associate w/ DNA, like histones
|
|
Heterochratin vs. Euchromatin
|
Heterochromatin:
|
|
Telomere
|
Repeating unit (TTAGGG) at the end of DNA, which saves DNA from being lost through repeated replication, since DNA polymerase can't go all the way to the end of a chromosome. Very stable because of lots of C to G bonds (3 H bonds each)
|
|
Centromere
|
Region of DNA found in center of chromosomes. Sites of constriction that form noticeable indentations. Composed of heterochromatin, w/ lots of C to G bonds (very stable). Helps sister chromatids stay connected during mitosis until they are pulled apart by microtubules in anaphase.
|
|
Prokaryotic vs. Eukaryotic DNA Replications
|
|
|
Semiconservative Replications
|
DNA replication is semiconservative because half of the original parent strand is in each of the 2 daughter strands
|
|
Everything in Molecular Biology is 5' to 3' (EXCEPT DNA POLYMERASE'S READING DIRECTION)
|
5' to 3':
|



