Cards In This Set
| Front | Back |
|
3 Categories of Glasgow Coma Scale. What is the maximum score? What is the threshold for severe injury?
|
O
Eye Opening (degree of stimuli
needed to open eye)
o
Verbal Response (quality of
verbal response from patient)
o
Motor Response (obeying
commands & responding to pain)
·
Maximum Score 15, < 8 =
severe injury
|
|
Define: Visualanosognosia (and location of brain damage)
|
Patient
is completely blind but acts as if sighted (tries to walk through walls,
collides into objects)... Damage in bilateral occiptal lobes.
|
|
4 Types of Blindsight
|
1)
Action-Blindsight
o
Most common
o
Able to act accuractely upon
blind field stimuli (e.g. by pointing, grasping, saccading)
2)
Attention-Blindsight
o
Riddoch Phenomenon à ‘sense’ or ‘feel’ something moving
3)
Agnosopsia
o
Can discriminate form and
wavelength above chance level
4)
Affective Blindsight
o
Can ‘sense’ something’s there
if there is a face with fearful expression
|
|
7 Tests for Blindsight
|
1)
Forced Choice
o
Patients must make choice of
“seeing” or “not seeing” in blind field
2)
Saccades & Points @ Target
o
Able to point at or follow
target with eyes
3)
Posting & Grasping
4)
Form Perception & Picture
Completion
5)
Semantics & Word-Perception
6)
Affective Blindsight &
Audio-Visual Binding
o
Covert recognition of facial
expressions (fearful gives best response) applies only to faces, not images of
emotional scenes (disasters, tragedies)
o
AV binding à face recognition works even better when given audio track that is
congruent with emotion on face (scary music and scared face)
7)
Neuroimaging Evidence
o
Affective Blindsight à fMRI shows activation of amygdale
|
|
Define: Hemineglect (and where is brain damage?)
|
Deficit in attention to left side of body (all aspects, both visual scene and physical body). Deficit in mental imagery on left side as well (recalling scenes). Damage to Right-Parietal
Lobe
|
|
What causes Viewer-Centered Neglect?
|
Hypoperfusion of Right Angular Gyrus & Supramarginal Gyrus
|
|
What causes Stimulus-Centered Neglect?
|
Hypoperfusion of Right Superior Temporal Gyrus
|
|
What brain region is used in high level searches?
|
Superior parietal cortex
|
|
Explain 'rivalry' phenomena in Hemineglect
|
Patient cannot count fingers in left visual field if fingers also in right visual field... can present if one at a time.
|
|
What are features of a vegetative state?
|
Sleep-Wake Cycles, Eyes occasionally open/Wandering, No awareness of self or environment
|
|
What is "Locked-in Syndrome"? What happens when they are asked to imagine moving.
|
Awake/Aware, cannot talk or move... can move eyes. In total locked in syndrome, no eye movement.Shows activation in supplementary motor areas when asked to imagine moving.
|
|
Draw out table comparing Coma, Vegetative State, Minimally Conscious State, Locked-in syndrome.
|
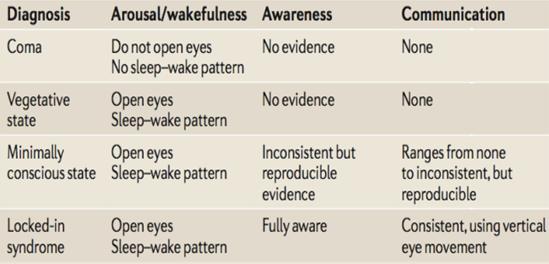 :) |
|
What are the 3 eye reflexes?
|
1) Pupillary Light Reflex2) Corneal Reflex (blink if touch cornea)3) Oculocephalic Reflex (turn head right, eyes move left)
All absent in coma. |
|
What are 2 breathing patterns associated with brain damage? Identify the brain damage.
|
1) Cheyne-Stoke's Breathing (cerebral cortex damage)2) Apneustic Breathing (pons lesion)
|
|
What are the 2 body postures associated with brain damage? Identify where the damage occured.
|
1) Decorticate Posture (cortex)- Elbows flexed- Clenched fingers- Legs & Feet extended2) Decerebrate Posture (brain stem)- Elbow extended- Clenched fingers- Legs & feet extended
|



