Cards In This Set
| Front | Back |
|
Name the (4) main stages of development
|
FertilizationCleavageGastrulationOrganogenesis
|
|
What occurs during Fertilization?
|
The sperm and the egg meet to produce the zygote
|
|
What is the principle purpose of Cleavage?
|
Cell division occurs to produce the blastula. The blastula is the hollow ball of cells from which the organism develops.
|
|
What occurs during Gastrulation?
|
During gastrulation, formation of germ cell layers occurs as well as the primitive gut. Gastrulation is a morphogenetic process that involves a dramatic rearrangement of the cells of the blastula.
|
|
What occurs during Organogenesis?
|
The formation of organs and tissues.
|
|
How are the Anterior-Posterior axis determined? When are they determined in many species (not humans)?
|
The Anterior-Posterior axis are determined by the uneven distribution of substances in the cytoplasm including specific mRNAs, proteins and yolk. The combination of all these cellular materials are called cytoplasmic determinants.
In many species (not including humans) this determination of anterior-posterior axis occurs prior to fertilization of the egg by the sperm. |
|
Define the vegetal pole and describe its appearance.
|
The vegetal pole is defined as the side of the zygote with a greater concentration of the yolk (stored nutrients)This pole is characterized by its yellow color because of lack of dark pigment granules.
|
|
Define the animal pole and describe its appearance.
|
The animal pole is defined by the side of the zygote where the yolk is less concentrated, and is also the site of where the polar bodies of oogenesis bud from the cell.The animal pole is characterized by its dark color as a result of a high concentration of dark pigment granules in the region.
|
|
When is the Dorsal-Ventral Axis established?
|
The Dorsal-Ventral Axis is established after fertilization
|
|
Why is their rearrangement of the cytoplasm after fertilization? What does this rearrangement form?
|
 After fertilization, the plasma membrane and cortex rotate towards the point of sperm entry.(see picture) this occurs so that the point of entry of the sperm is directly parallel with the regions defining the vegetal pole (yellow) and the animal pole (blue). The rearrangement of the cytoplasm causes the exposure of the grey crescent. |
|
What does the grey crescent define?
|
The grey crescent, formed from the rearrangement of the cytoplasm, defines the dorsal side of the embryo
|
|
How is the dorsal side of the embryo determined in terms of cytoplasmic determinants?
(general explanation) |
The way in which different proteins, kinases and inhibitors are distributed within the cell lead to different cellular processes that help to define the dorsal side of the embryo.
|
|
On slide 5, what did the blue, red, and peach colors represent?
(only what they represent. example: green = receptor ) |
The blue represent GSK-3 which is a protein kinase. The protein kinase phosphorylates the peach
The red represents a GSK-3 inhibitor which stops the phosphorylation of the peach The peach represent b-catenin, a component of cell-cell signaling that defines the dorsal side as development proceeds |
|
Where are the blue, red, and peach colors located respectively? Why is this significant?
|
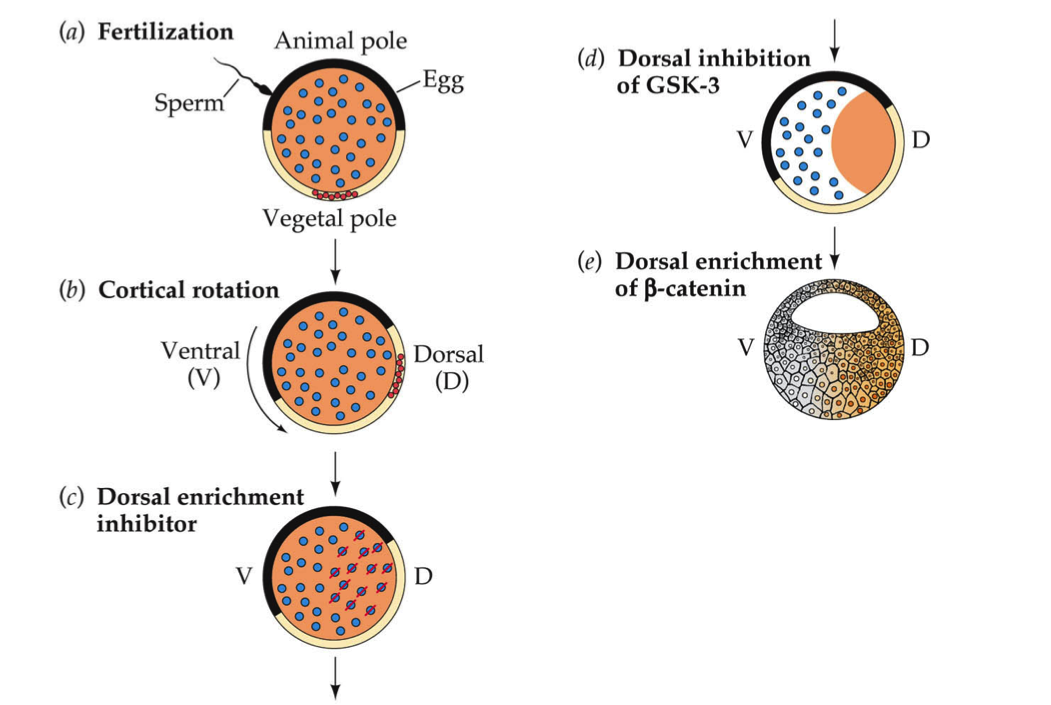 In the zygote, the red GSK-3 inhibitors are located near the vegetal pole. They are located here to stop the phosphorylation action of the blue GSK-3 kinases of the peach b-catenin. This is important because the presence of b-catenin defines the dorsal end. Conversely, there is a low concentration of the red GSK-3 inhibitors on the ventral side of the zygote because the cell wants the blue GSK-3 kinases to phosphorylate the peach b-catenin. The phosphorylation of the b-catenin leads to its degradation. Thus, there is no b-catenin on the ventral side (which is good, because b-catenin defines the dorsal side). |
|
How are the right-left axis determined? When are they determined?
|
The right-left axis are determined after the anterior-posterior and dorsal-ventral axis are established. The right-left are fixed by the first cleavage, or cell division, which bisects the grey crescent.
|



