Cards In This Set
| Front | Back |
 Islam |
An Arabic term meaning “submission to God’s will,” it is used to describe the religion based on the Qur’an and Muhammad’s teachings. |
|
Muhammad (570-632)
|
According to Islam, Muhammad begins receiving divine messages from angel Gabriel in 610. He leaves his
hometown of Mecca in 622, returns in 630 |
|
Qur’an (Koran)
|
Seen as direct word of God as revealed to Muhammed through the angel Gabriel. In this way it differs from the
Old Testament and New Testament |
|
Seen as direct word of God as revealed to
Muhammed through the angel Gabriel. In this way it differs from the Old Testament and New Testament |
-shahada (avowal of faith)
-prayer (five times daily) -alms -fasting during Ramadan -hajj |
|
Shahada
|
-(avowal of faith)
the act of bearing witness to God’s unity is the basic act of Muslims |
|
Prayer
|
-(five times daily)
the format of the prayer comes from the teachings of Muhammad; purity of the body and place of prayer is required |
|
Alms
|
A certain percentage of income is given to the needy
|
|
Fasting during Ramadan
|
Refraining from eating, drinking, smoking, and sexual activity from dawn to sunset during the ninth month of the
Islamic lunar calendar |
|
Hajj
|
Pilgrimage to Mecca at least once for all Muslims who have the means to do so
|
|
Ulama
|
-leaders in Islam
-they perform no tasks that cannot be performed by any adult Muslim -means “the learned” and these figures preserve and maintain knowledge |
 Mosque |
-place of communal prayer -term derived from the Arabic masjid, meaning place of prostation -often the focal point of a complex that includes hospitals, madrasas (religious schools), shelters for travelers, and other buildings -In addition to providing a place for prayer, mosques typically serve as educational centers |
|
Jami
|
-Large communal mosques
-often called Great Mosques or Friday Mosques |
|
Elements of Mosque
|
-minaret (distinctive architectural features that are generally tall spires with onion-shaped or conical crowns)
-courtyard -covered prayer hall -minbar (a speaker's stand in the mosque where the leader of prayer stands to deliver sermons) -qibla (is the direction that should be faced when a Muslim prays during salah) -mihrab (a semicircular niche in the wall of a mosque that indicates the qibla) |
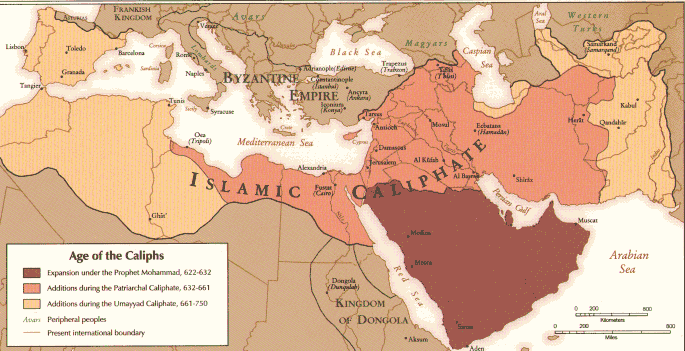 Al-Andalus: Islam on the Iberian Peninsula Expansion of the Islamic Caliphate |
-Umayyad Dynasty: 661-750; capital at Damascus. After Abbasids capture Damascus, an Umayyad prince flees to Spain and begins the Islamic age there. -Abbasid Dynasty: 750-1258; capital at Baghdad |
 Islam and the Mediterranean circa 1000 |
Al-Andalus was the Arabic name for areas on the Iberian peninsula (an area including modern-day Spain and Portugal). From the 7th century until 1492, Islamic rulers controlled parts of this region |



