Cards In This Set
| Front | Back |
|
5.1.1 define electric potential difference
|
-electric potential difference: work done per unit charge to move a positive test charge between A and B- joule / coulomb = volt
|
|
5.1.2 Determine the change in potential energy when a charge moves between two points at different potentials.
|
-The change in the electrical potential energy = the work done-Moving from point A (low EP) to point B (hight EP) makes charge q gain electrical potential energy -Potential energy = F * d = E * q * d
|
|
5.1.3 Define the electronvolt
|
- the energy acquired by an electron as it moves through a potential difference of 1 volt. - 1 eV = 1.6 * 10-19J
|
|
5.1.5 Define electric current
|
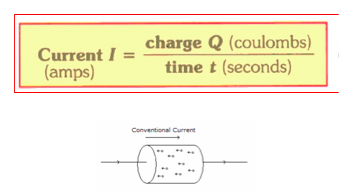 - The flow of charge particles through a material when a potential difference is applied across it.-Rate of flow of charge -Unit : Ampere (A)-conventional <-> electron flow |
|
5.1.6 Define resistance
|
 - a measure of how difficult a charge can flow in a material - Unit: Ohms |
|
5.1.8 State Ohm's Law
|
- provided that the physical conditions such as temperature are kept constant, the resistance is constant over a wide range of applied potential difference and therefore the potential difference and therefore the potential difference is directly proportional to the current -potential difference (a) current.- Voltage = current *Resistance
|
|
5.1.9 Compare Ohmic and non-ohmic behavior
|
 - in ohmic behavior, V and I are not proportional to each other. - in non-ohmic behavior, V and I are not proportional to each other. |
|
5.1.10 Derive and apply expressions for electrical power dissipation in resistors.
|
-electrical power is the rate that an electrical device uses energy. P = Et = I2R - V2R
|
|
5.2.1 Define electromotif force (emf).
|
The amount of energy per unit charge supplied to a circuit by a power source.
|
|
5.2.2 Describe the concept of internal resistance
|
 When a battery supplies a current to an external circuit it gets warm. This is due to the battery having a small internal resistance. |
|
5.2.4 Draw circuit diagrams
|
 SEE IMAGE |
|
5.2.5 Describe the use of ideal ammeters and ideal voltmeters
|
Ammeter: - measure current- in series- minimum resistance- ideal ammeter
Voltmeter:- measure voltage- in parallel- maximum resistance- ideal voltmeter |
|
5.2.6 Describe a potential divider
|
 SEE IMAGE |
|
5.2.7 Explain the use of sensors in potential divider circuits
|
 SEE IMAGE |
|
6.1.1 State Newton's universal law of gravitation
|
Every material particle in the Universe attracts every other material particle with a force that is directly proportional to the product of the masses of the particles and that is inversely proportional to the square of the distance between them
|



