Cards In This Set
| Front | Back |
|
8.1.1:
State that thermal energy may be
completely converted to work in a
single process, but that continuous
conversion of this energy into work
requires a cyclical process and the
transfer of some energy from the
system.
|
Simple stating of objective.
|
|
8.1.2:
Explain what is meant by degraded
energy.
|
Students should understand that, in any process
that involves energy transformations, the energy
that is transferred to the surroundings (thermal
energy) is no longer available to perform useful
work.
|
|
8.1.3: Construct and analyse energy
flow diagrams (Sankey diagrams)
and identify where the energy is
degraded.
|
 It is expected that students will be able to construct flow diagrams for various systems including those described in sub-topics 8.3 and 8.4. |
|
8.1.4: Outline the principal mechanisms
involved in the production of
electrical power.
|
Students should know that electrical energy may
be produced by rotating coils in a magnetic field.
Any force that will spin a turbine (e.g. steam from water heated by burning fossil fuels, wind, waves, etc. Turbine causes generator to produce electricity from electromagnetic induction. |
|
8.2.1: Identify different world energy
sources.
|
Students should be able to recognize those sources
associated with CO2 emission.
Students should also appreciate that, in most
instances, the Sun is the prime energy source for
world energy.
Different Sources: Coal Oil Natural gas Nuclear Solar Wind Wave Tidal Hydroelectric Geothermal |
|
8.2.2;
Outline and distinguish between
renewable and non-renewable
energy sources.
|
1. Renewable Energy
Source – source of energy that cannot be used up (eg.
–hydroelectric, photovoltaic cells, active solar heaters, wind, biofuels) (NOTE:
In most instances, the Sun is the primary energy source for world energy.)
2. Non-renewable
Energy Source – source of energy that can be used up (eg. – coal, oil, natural gas, nuclear).
|
|
8.2.3:
Define the energy density of a fuel.
|
The
ratio of the energy released from the fuel to the mass of the fuel consumed
Energy density is measured in J kg–1. |
|
8.2.4:
Discuss how choice of fuel is
influenced by its energy density.
|
Greater energy density = greater energy per
unit mass/volume = more energy for same mass/volume = more efficient
These factors influence choice based on energy density alone. |
|
8.2.5:
State the relative proportions of world
use of the different energy sources
that are available.
|
 See image. |
|
8.2.6:
Discuss the relative advantages and
disadvantages of various energy
sources.
|
 See image. |
|
8.3.1:
Outline the historical and
geographical reasons for the
widespread use of fossil fuels.
|
Students should appreciate that industrialization
led to a higher rate of energy usage, leading to
industry being developed near to large deposits of
fossil fuels.
Industrial Revolution had large energy demands, increasing population growth Household appliances and heavy industrial machinery require large amounts of energy, steam engine and other inventions Geographical Fossil fuel reserves abundant in most continents Industrial developments centered around fossil fuel deposits |
|
8.3.2:
Discuss the energy density of fossil
fuels with respect to the demands of
power stations.
|
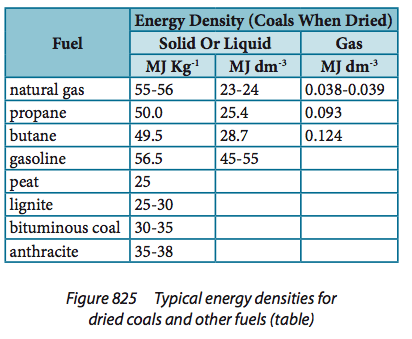 Students should be able to estimate the rate of fuel consumption by power stations. People demand power all the time. Used even when we sleep. |
|
8.3.3:
Discuss the relative advantages and
disadvantages associated with the
transportation and storage of fossil
fuels.
|
Coal
Advantages
-simple storage
-safe
Disadvantages
-low energy density
Oil
Advantages
-convenient location of rigs
Disadvantages
-oil spills and leaks
-vulnerable to terrorist
activities and natural disasters
Natural gas
Advantages
-high energy density
Disadvantages
-expensive gas line setup and
maintenance costs
|
|
8.3.4:
State the overall efficiency of power
stations fuelled by different fossil
fuels.
|
Approximate values only.
Coal - 35Oil – 38% Natural gas – 45% |
|
8.3.5:
Describe the environmental problems
associated with the recovery of fossil
fuels and their use in power stations.
|
Coal
Recovery
-strip mining (sulfuric acid and soil erosion)
-mining hazards (toxic gas and tunnel cave ins)
Oil and Natural gas
Recovery
-extensive time to map and plan construction
-expensive construction and maintenance costs
-possible spill and leak risks
Power Station Use
-air pollution (CO2, CO, SO2,
soot, Nitrogen oxides emissions)
|



