Cards In This Set
| Front | Back |
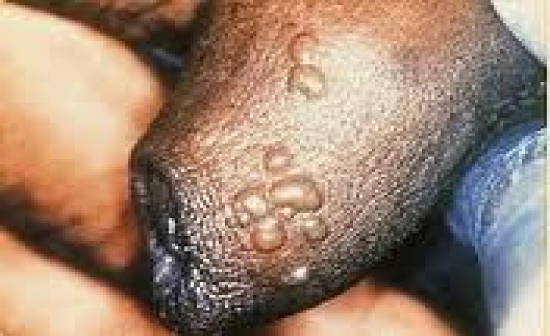 26 y/o male pt comes in with regional lymphadenopathy, fever and a vesicular rash on his genitals what is the most probable virus? what other virus can it be? What would the dr get if he didnt wear gloves? Serios complication? Where does the latent infection live? |
HSV2 (genital herpes), could be HSV1 (oral)
DR: Herpetic Whitlow (painful finger infection) Complications: Encephalitis (HSV-1 is teh most common viral cause), disseminates in immunocomp α latent in dorsal root ganglia |
|
What is TORCHES? Name them.
|
TORCHES= viral infections that can cross placents
TOcoplasmosis Rubella Cytomegalovirus HErpes, Hiv Syphilis |
 <5 y/o child with fever, malaise and vesiculopapular rash that spread from trunk to extremities, non-umbilicates superficial lesions at different developmental stages. Virus? Dx? Complication? Latent phase is where? Reactivation? |
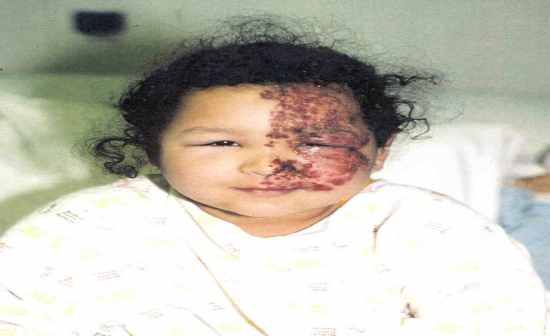 Varicella Dx: giant cells precent on slide of lesion Complications:hepatits, pneumonitis, encephalitis, secondary bact-> all more common in adults Latent: α latent in dorsal root ganglia Reactivation: Shingles (zoster), reactivation of sensory nerves, usually confined to unilateral dermatomes |
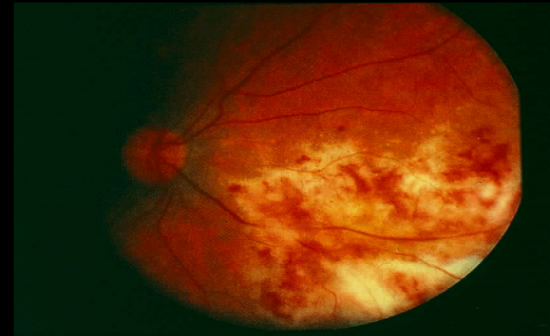 HIV+, IV drug user pt comes in after having a mono-like illness with a negative monospot test. Pts CD4<100 and now has bilateral vision problems probelms What is the Virus? What is the ocular syndrome? What is teh other severe syndrome this virus can cause? |
CMV (β: monocytes latency)
Necrotizing chorioretinitis Congential CMV (if mom's first infection) |
 Child <1 with slight fever and the rash below that lasted 6 day. Generally self-limits and no tx indicated. Name the virus |
HHV6 β (Roseola infantum)
|
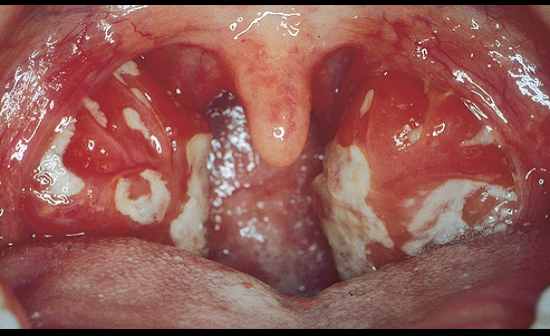 Cervial chasin lymphadenopathy sore through fever, splenomegaly and is very tired with hemolytic anemia. Virus? What is the most common presentation of this virus? Dx test? What cells does the virus infect? Major complcations? |
Epstein-Barr Virus (gamma herpes virus)
Commonly asymptomatic (90% adults have ab) Monospot test for EBV ab Cells: B cells Major complications: splecnic rupture, hemolytic anemia, Burkitts lymphoma, hodgkins lymphoma, CNS lymphoma, naso pharngeal carcinoma |
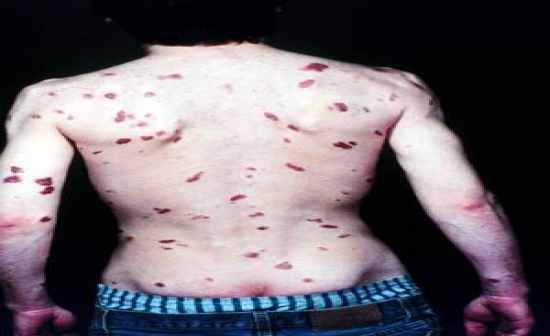 Indistiguishable from EBV except by PCR. Present in 90% of all HIV associated Kaposi’ sarcom. |
HHV8 γ
|



