Cards In This Set
| Front | Back |
|
TVI is similar to peak velocity. However, TVI may be more accurate. May see peak velocity given on the boards.
|
TVI is similar to peak velocity. However, TVI may be more accurate. May see peak velocity given on the boards.
|
|
How can you use echo to calculate cardiac out put?
|
|
|
What is the simplified Bernoulli Equation?
|
 P=(4V2)2P=pressureV=velocity To maintain flow continuity, flow speed must increase through a stenosis.In conjunction with this, the pressure drops in the stenosis |
|
How do you calculate the AV area using the continuity equation?
|
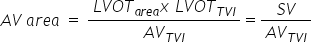 |
|
How do you calculate the LVOT area?
|
Area of a circle = ∏r2Therefore, LVOT area = ∏ x (1/2 LVOT diameter)2
|
|
What is the short cut for calculating the AVA?
|
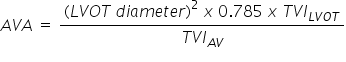 Remember the TVI can be substituted for peak velocity Remember the TVI can be substituted for peak velocity |
|
Calculate the AV area based on the following:AV TVI = 105cmMean Gradient = 35mmHgLVOT TVI=30LVOT =2.4LV EF=60%
|
 1.3cm2Remember that Peak velocity can be substituted for TVI. |
|
How is aortic stenosis graded?
|
 |
|
How is the aortic valve assessed by echo?
|
Valve morphologyPeak and mean gradientsAortic valve area (Continuity equation and planimetry)Dimensionless index
|
|
What is dimensionless index?
|
This is the ratio between the LVOT velocity and AV velocity.When this ratio is <0.25, this is generally consistent with severe AS.
|
|
What are the pitfalls of assessing AS with echo?
|
 Doppler angle
|
|
Why should you not use the femoral sheath side arm as a surrogate for central aortic pressure?
|
 There is a temporal delay in the peripheral pressure.There is also a pressure “overshoot”These will lead to problems with aortic valve gradient. |
 What is this tracing showing? |
This is a simultaneous LV, Ao, and FA tracing illustrating how erroneous the FA tracing is (temporal delay and pressure overshoot).
|
|
In an invasive hemodynamic AS study, why should the mean gradient be used instead of the peak to peak gradient?
|
The peak to peak gradient is not simultaneous and is therefore not physiologic.
|
|
What is the Gorlin Formula?
|
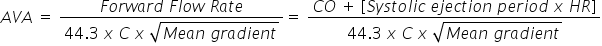 |



