Cards In This Set
| Front | Back |
|
What are to two key control systems?
|
Nervous and Endocrine
|
|
Characteristics of the Nervous System
|
Fast-acting control system
reponds to internal and external changes (basis of homeostasis) Activates muscles and glands |
 Fill in the gaps |
 |
|
Draw a diagram of the organisation of the nervous system
|
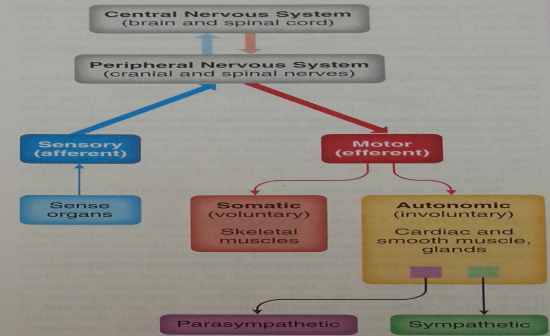 |
 Fill in this image |
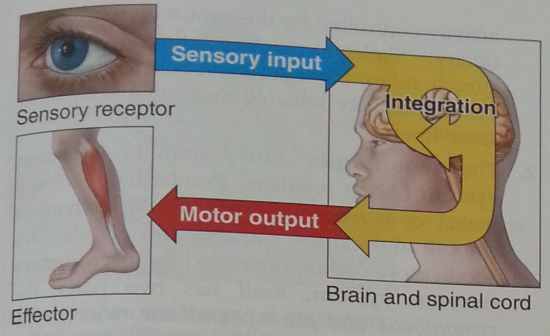 |
 Fill in the image |
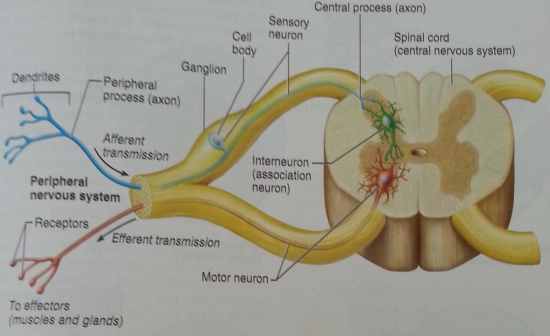 |
|
Draw a nerve cell
|
 |
|
What is the sympathetic function of the nervous system?
|
Sympathetic - Fight, Flight, Fright
Remeber as the "e" division = exercise, excitement, emergence and embarrasement |
|
What kind of things does the sympathetic divison of the nervous system do?
|
Increses heart rate and force of contraction
dilation of airways in lungs decreased digestive acitivity contriction of blood vessels in viscera and skin / dilation of blood vessels in skeletal muscle and heart |
|
What is the Parasympathetic Function of the nervous system?
|
Resting and digesting
Conserves energy maintains daily necessary body functions Remeber as the "D" division: disgestion, defecation and diuresis |
|
How does the parasympathetic division effect the body?
|
Decreases heart rate
constriction of airways in lungs increased digestice activity little or no effect on blood vessels |
|
What is a nerve cell?
|
Neuron = Cells specialised to transmit messages
|
|
What are the major regions of a neuron
|
Cell body - nucelus and metabolic center of the cell
Processes - fibers that extend from the cell body Dendrites - conduct impulse toward the cell body Axon - conduct impluses away from the cell body Schwann cells - produce myelin sheaths Nodes of Ranvier - gaps in myelin sheath along the axon |
|
Describe the location of the axon.
|
Starts at the axon hillock and ends at the axonal terminals
|
|
Where an what is the axon terminal?
|
Axon terminal contain vesicles with neurotransmitters and is at the end of an axon. Axon terminals are seperated fro the next neuron by a gap
|



