Cards In This Set
| Front | Back |
|
Definition of Constitutional, Configurational and Conformational Isomerism
|
Constitutional isomerism: Isomers whose atoms have different connectivity.
Configurational isomerism: describes the particular arrangement of atoms (groups) in space that are connected to a central atom.
Conformational isomerism: The arrangements of atomic positions in a molecule that are generated by rotation about a single bond.
|
|
List the types of stereoisomerism.
|
Enantiomers and diastereomers
|
|
Definition of enantiomers (give examples)
|
Enantioners are stereoisomers that are mirror images of each other
|
|
Opical activity: The equation for specific rotation.
|
|
|
The structure of D- and L-glyceraldehydes: the principles for relative configurations.
|
 D(+)- and L(-) glyceraldehydes |
|
The Structure of R- and S-lactic acid: the principles for absolute configurations.
|
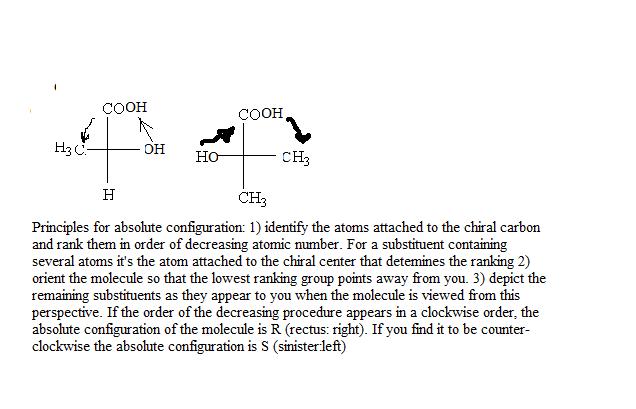 The structure of R- and S-lactic acid |
|
Definition of diastereomers.
|
 Diasteriomers are stereoisomers that are not mirror reflections of each other. |
|
Definition of a racemic mixture.
|
A racemic mixture is an equimolar mixture of enantiomers. It is optically inactive and does not cause a rotation in the plane polarized light
|
|
Strucure and optical activity of meso-tartaric acid
|
 The molecule is optically inactive. The top half cancels out the bottom half. Therefore the molecule as a whole is achiral and does not cause a rotation of plane polarized light |
|
List the methods for the resolution of racemic mixtures.
|
Resolution is basically the seperation of a racemic mixture into its enantiomeric components.
3 methods of resolution: Crystallization, chromatography and the use of enzymes.
|
|
Homologous series of alkanes (containing 1 to 10 carbon atom): structure and name for each.
|
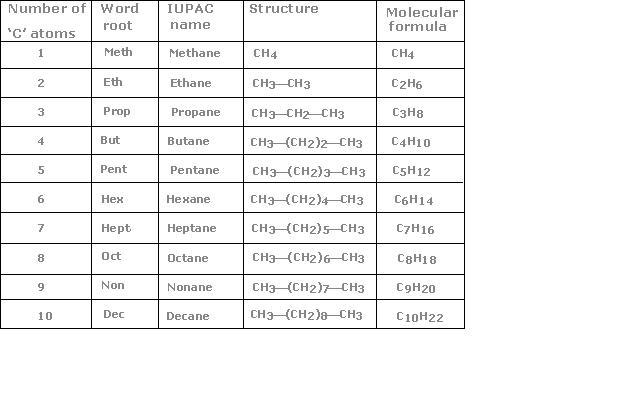 Structure and name for each alkane |
|
Structure of staggered and eclipsed ethane
|
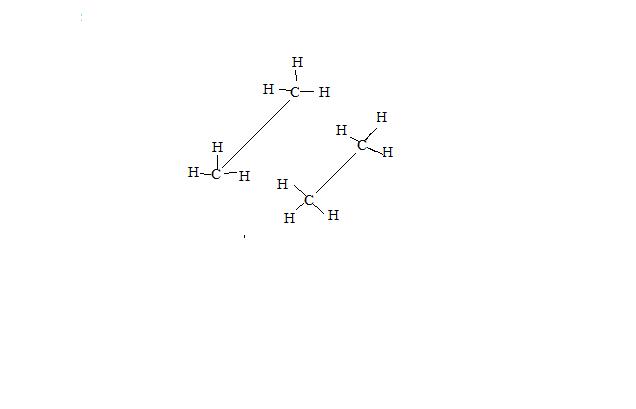 Structure of staggered and eclipsed ethane |
|
Structure and name for the isomers of butane.
|
 N-butane, isobutane |
|
Structure of 2,3-dimethyl-butane.
|
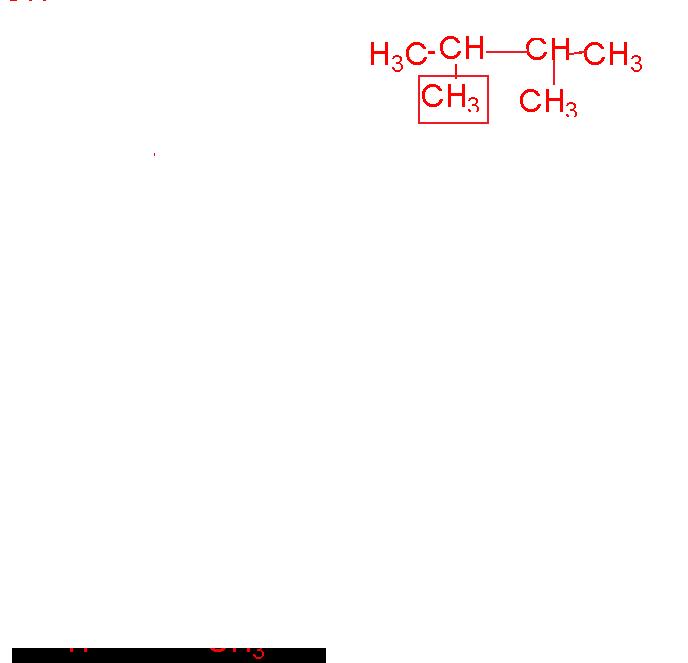 2,3-dimethyl-butane |
|
Structure of 3-ethyl-3-methyl-hexane
|
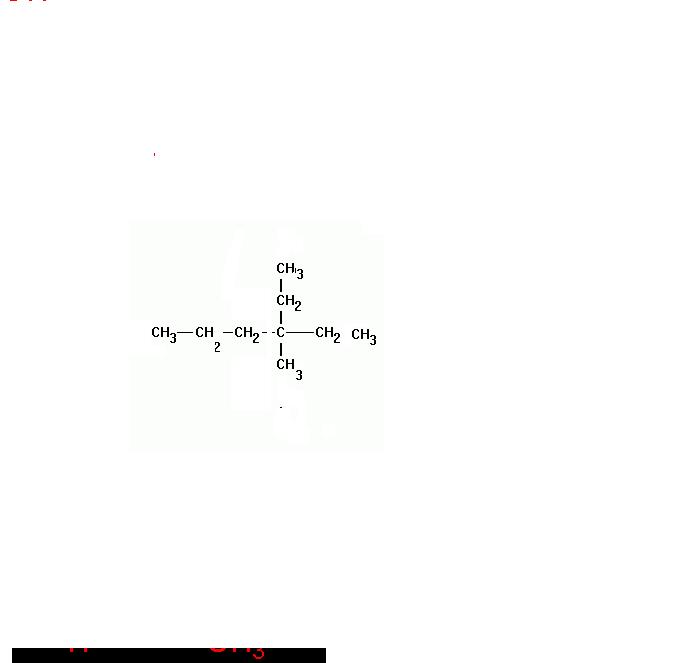 3-ethyl-3-methyl-hexane |



